Table of Contents
Top 5 Data Governance Use Cases: Essential Applications for 2026
💡 QUICK ANSWER: What Are Data Governance Use Cases?
Data governance use cases are practical applications where governance frameworks solve specific business challenges. The most critical use cases include:
- Regulatory Compliance: GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA adherence with automated audit trails
• Data Privacy Protection: PII identification, access controls, and encryption
• Collaborative Analytics: Breaking down data silos for cross-functional insights
• Business Glossary Creation: Standardized terminology across the organization
• Centralized Access Management: Role-based controls and security enforcement
• Data Quality Improvement: Validation, cleansing, and accuracy standards
• Master Data Management: Single source of truth for critical business entities
• AI/ML Enablement: Trusted data for models, bias detection, explainability
Each use case addresses specific pain points where ungoverned data creates compliance risk, inefficiency, or poor decision-making.
It’s almost impossible to emphasize how important data is to both people and industry. Not only is data at the heart of most business operations, but there is also increasing pressure from customers to have visibility of what’s being stored, how, and why.
Despite this, about 40 percent of enterprise data is“either inaccurate, incomplete, or unavailable,” which leads to an estimated annual loss of approximately $14 million.
According to Gartner, 75% of the global population now has personal data covered by privacy regulations, with 85% expected by 2026.
Yet only 42% of data leaders have proper governance frameworks in place, leaving organizations exposed to compliance violations, security breaches, and missed opportunities.
This is why it’s so vital to have a clear understanding of what data governance is and the different ways you should implement it.
If you’re unsure of what data governance is, you should read our Ultimate Guide, but for now, here is how we define it:
Data governance is the process of organizing, securing, managing, and presenting data using methods and technologies that ensure it remains correct, consistent, and accessible to verified users.
Data governance isn’t as complicated as most people think, but it’s still important to have a clear idea of the primary use cases. This helps you effectively implement and improve your existing and future data initiatives.
In this article, we will cover the following Data Governance use cases:
- Collaborative analytics or building new data products
- Data privacy compliance
- Data discovery and data literacy provisions
- Create a centralized repository of all standardized business terms
- Centralized data access management
This guide explores five proven data governance use cases that deliver immediate business value, with real examples from companies like Naranja X and Upwork, plus implementation guidance for 2026.
Are you ready to create a sturdy case for the ROI of a data governance program? Download OvalEdge Use Cases
Data Governance in 2026: New Priorities and Trends
The data governance landscape has evolved significantly since 2022. Organizations now face new challenges and opportunities driven by AI adoption, regulatory expansion, and architectural shifts.
1. AI and GenAI Governance Takes Center Stage
The explosion of generative AI tools (ChatGPT, Claude, Midjourney) has created urgent new governance requirements:
Training Data Quality: AI models require governed, high-quality datasets to avoid hallucinations and bias. According to Gartner, 80% of AI projects fail due to poor data governance.
Model Explainability: Data lineage tracks which data influenced AI decisions, enabling regulators to understand how models use customer information.
Bias Detection: Governance identifies underrepresented groups in training data and tests for algorithmic discrimination.
Prompt Security: Protecting against prompt injection attacks and data leakage through LLM interactions.
Organizations implementing AI report that data governance is their number one bottleneck. Without trusted, governed data, AI initiatives deliver poor results or fail.
2. Real-Time Governance for Streaming Data
Traditional batch-based governance no longer meets modern needs. Event streaming platforms (Kafka, Kinesis) require real-time PII detection, live dashboard analytics demand instant data validation, and IoT sensors generate billions of data points needing automated governance.
Modern platforms like OvalEdge now support real-time data catalog updates and streaming lineage tracking.
3. Privacy Regulations Expand Globally
New laws emerged in 2023-2024, creating a complex compliance landscape:
- EU AI Act: First comprehensive AI regulation (2024)
- US State Laws: 12+ new state privacy laws beyond California
- China PIPL: Personal Information Protection Law enforcement
- India DPDP Act: Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023
Compliance burden increased 300% for multinational companies since 2022. Average annual privacy budgets for large organizations now exceed $2.5 million, with many enterprises allocating $5-10M as regulations expand globally.
4. Data Mesh and Federated Governance
Organizations are shifting from centralized to federated governance models. Data mesh architecture treats data as products owned by domain teams, enabling self-service with guardrails. This requires new governance tools that scale across distributed teams while maintaining enterprise standards.
5. ESG and Sustainability Data Governance
Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) reporting now requires rigorous data governance for carbon tracking (Scope 1, 2, 3 emissions), supply chain transparency, and regulatory requirements like EU CSRD and SEC climate disclosure rules. Poor ESG data governance risks greenwashing accusations and significant fines.
Use Case 1: Collaborative Analytics and Building New Data Products
When you’re building a new data product, you need your data to be easily accessible, not just to the data team, but also to other business users.
The Challenge
Data silos kill innovation. When marketing, sales, operations, and finance each maintain separate databases with no shared access or standards, building comprehensive analytics becomes impossible.
Common problems:
- Marketing can't access sales pipeline data to measure campaign effectiveness
- Product teams lack customer support data to prioritize feature development
- Finance can't reconcile operational metrics with revenue data
- Data scientists spend 60-80% of their time finding and preparing data instead of building models
According to McKinsey research, companies with mature data governance are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 6 times more likely to retain them. Breaking down silos through governance creates a competitive advantage.
How Data Governance Solves This
Data governance removes blockers by making it easy for anyone in the company to analyze data meaningfully without technical training or waiting for data team support.
3 Core Capabilities:
- Self-Service Data Discovery
- Business users search a centralized data catalog to find datasets
- No SQL knowledge required - intuitive interface like Google search
- Preview data, understand field meanings, check quality scores
- See who owns data and request access with one click
- Business Context and Definitions
- Every dataset has clear business descriptions, not just technical metadata
- Field-level documentation explains what the data means
- Data quality indicators show reliability
- Usage examples demonstrate how others analyze the data
- Secure Access with Governance
- Role-based permissions ensure users see only authorized data
- Automated workflows route access requests to data owners
- Audit trails track who accessed what data and when
- Compliance is maintained while enabling self-service
Real Example: Naranja X Transforms Data Governance
Challenge: Naranja X, a leading fintech company in Latin America with 5+ million customers, struggled with data scattered across 15 siloed systems. Their data team could only govern 10% of critical customer and transaction data, leading to compliance risks, regulatory exposure, and decision-making delays that cost millions annually.
Solution: Using OvalEdge's automated data catalog and governance workflows, Naranja X:
- Discovered and classified 10,000+ data assets across all systems in 8 weeks
- Implemented role-based access controls with automated enforcement
- Automated PII detection and masking for GDPR and local privacy compliance
- Built a company-wide business glossary with 500+ standardized financial terms
- Enabled self-service analytics for 200+ business users
Results:
- 70% of data warehouses are now under governance (up from 10%)
- Compliance audit preparation time reduced from 6 weeks to 3 days (93% faster)
- Data discovery time for analysts reduced by 65%
- Zero compliance violations in 18 months post-implementation
- $2.3M saved annually in reduced audit costs and avoided fines
What's New in 2026: Collaborative analytics now includes AI assistance. Data teams use GenAI tools to generate SQL queries, create visualizations, and interpret results. But ungoverned data fed to LLMs creates security risks and hallucinations. Modern governance ensures only trusted, cataloged data powers AI analytics.
It also makes it significantly easier for the data team to collaborate on specific projects. Data governance tools make it simple to analyze data sets simultaneously, then share findings and results with key stakeholders.
Fintech company Naranja X found that by implementing OvalEdge, they now get a much wider view of their product data:
Before OvalEdge integration, the Naranja X data team only governed a small percentage of the company’s data. Now 70% of the organization’s data warehouse is governed.
Related: What is Data Mesh? Principles & Architecture
Use Case 2: Data Privacy Compliance (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA)
Over the last few years, there has been much more emphasis on how our personal data is stored and what data is kept. And rightly so!
The Challenge
Privacy regulations have exploded globally. Organizations now navigate 150+ data protection laws, each with different requirements, definitions, and penalties:
- GDPR: Fines up to €20M or 4% of global revenue
- CCPA: $7,500 per violation
- HIPAA: $1.5M maximum annual penalty
- Brazil LGPD: 2% of revenue up to $50M
The average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million in 2023 (Ponemon Institute), with regulated industries facing additional compliance fines. Without governance, tracking where sensitive data lives, who accesses it, and how it's protected becomes impossible.
How Data Governance Enables Compliance
Data governance provides the foundation for meeting regulatory requirements through automated discovery, classification, and protection of sensitive data.
3 Core Privacy Compliance Capabilities:
- PII Data Discovery and Classification
- Automatically scan all data sources: databases, files, cloud storage, SaaS applications
- Identify sensitive data: SSN, credit cards, health records, email addresses, phone numbers
- Tag and classify by sensitivity level (Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted)
- Track location across all systems with automated, continuously updated inventory
- Pattern recognition finds PII even in unstructured data and documents
- Right to Know (Data Access Requests)
- Search and retrieve all personal data for a specific individual across the enterprise
- Compile comprehensive reports within 30-day GDPR/CCPA deadline
- Automated data extraction across 100+ source systems without manual queries
- Generate formatted reports suitable for customer delivery
- Audit trail documenting who accessed data and when for compliance proof
- Right to Delete (Data Erasure)
- Identify all instances of personal data across enterprise, including backups
- Orchestrate deletion across databases, data warehouses, backups, and archives
- Verify complete removal with automated validation and deletion certificates
- Maintain tamper-proof compliance records for auditor review
- Handle complex data relationships and foreign keys automatically
- Consent Management
- Track customer consent for each data use purpose
- Enforce consent-based access rules automatically
- Update access when consent is withdrawn
- Generate consent audit reports for regulators
Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and IAPP have been put in place to protect customers’ PII (Personally Identifiable Information), but they also create a lot of risk for organizations.
Management consulting company Gartner predicts that 75% of the global population will have their personal data covered under privacy regulations over the next couple of years.
With the expansion of privacy regulation efforts across dozens of jurisdictions in the next two years, many organizations will see the need to start their privacy program efforts now. In fact, Gartner predicts that large organizations’ average annual budget for privacy will exceed $2.5 million by 2024.
Real Example: Upwork's CCPA Compliance Victory
Challenge: Upwork, the world's largest freelancing platform connecting 18+ million freelancers with businesses, faced strict CCPA compliance requirements. With user data spread across dozens of systems and hundreds of terabytes of historical data, manually identifying and managing personal information for data subject requests would have required a team of 20+ people working full-time.
Solution: Upwork implemented OvalEdge to automate PII discovery and management:
- Automated scanning identified PII across all 50+ production systems
- Classified data by sensitivity: Basic PII, Financial, Health, Biometric
- Tagged datasets containing California resident data for CCPA compliance
- Built automated workflows for Right to Know and Right to Delete requests
- Implemented data masking for non-production environments
Results:
- Identified, classified, and secured ALL sensitive data in just 3 weeks (vs. 6+ months manual)
- Reduced CCPA request processing time from 2-3 weeks to 4 hours (90% faster)
- Compliance risk reduced by 95% through comprehensive PII coverage
- Zero CCPA violations since implementation
- Scaled to handle 100+ data subject requests monthly without adding headcount
What's New in 2026: Privacy regulations have expanded dramatically. Organizations now navigate the EU AI Act (governing AI training data), China's PIPL, India's DPDP Act, and 12+ US state laws. Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) like differential privacy and homomorphic encryption are becoming governance requirements, not optional nice-to-haves.
Freelancing platform Upwork struggled to identify all the PII data stored across its various systems until it used OvalEdge. Using our data governance tools, they found, classified, and secured all their sensitive data in only a few weeks.
Related: Data Privacy Compliance: How to Ensure it and How it Can Benefit Your Business
Use Case 3: Data Discovery and Data Literacy Provisions
The Challenge
According to Harvard Business Review, 90% of business leaders cite data literacy as critical to organizational success, yet only 25% of employees feel confident in their data skills. This massive gap costs organizations millions in lost productivity and missed opportunities.
Common symptoms:
- Business analysts can't find the datasets they need without IT help
- Teams don't understand what data means or how to interpret it correctly
- Same questions get asked repeatedly because knowledge isn't captured
- Inconsistent definitions lead to contradictory reports and wrong decisions
- Onboarding new employees takes months due to lack of documentation
Without governance, tribal knowledge stays locked in individual heads. When key people leave, critical data understanding disappears with them.
How Data Governance Builds Data Literacy
Data governance creates a self-service environment where anyone can discover, understand, and use data confidently.
4 Data Literacy Components:
- Searchable Data Catalog
- Google-like search finds datasets by business term, not technical name
- Browse by domain: Customer data, Product data, Financial data, Operations
- Filter by data quality score, freshness, popularity
- See related datasets and recommended analyses
- 70% faster data discovery compared to manual methods
- Business Context and Documentation
- Plain language descriptions for every dataset and field
- Real-world examples showing how to use the data
- Quality indicators: Completeness, accuracy, timeliness scores
- Owner information: Who maintains this data and who to ask questions
- Lineage visualization: Where data comes from and where it goes
- Standardized Business Glossary
- Company-wide definitions of key terms prevent confusion
- Linked to actual data fields showing where terms appear
- Version history tracks definition changes over time
- Steward assignments ensure someone owns each definition
- Embedded Training and Guidance
- In-app tutorials for common tasks
- Best practice guides and tips
- Success stories from other teams
- Office hours and support channels
Real Example: Accounting Firm Scales Data Expertise
Challenge: A large international accounting firm with 1,000+ clients across 34 countries struggled with massive data literacy gaps. Only senior consultants (5% of staff) could effectively analyze client data.
Junior staff waited weeks for senior team members to run analyses, creating bottlenecks. Client delivery timelines slipped, and the firm couldn't scale without hiring expensive senior talent.
Solution: The firm implemented OvalEdge's data catalog and governance platform:
- Cataloged 5,000+ client datasets with business-friendly descriptions
- Created standardized definitions for 200+ accounting and audit terms
- Built guided workflows for common analysis tasks
- Documented 50+ analysis templates with step-by-step instructions
- Enabled self-service access with automated governance
Results:
- Junior staff can now perform 85% of analyses independently (vs. 10% before)
- Time to complete client deliverables reduced by 40%
- Senior consultant bottleneck eliminated, freeing them for complex work
- Onboarding time cut from 6 months to 6 weeks through documentation
- Client satisfaction scores increased 25% due to faster turnaround
- 3x growth in clients served without proportional headcount increase
- $4.5M annual savings in reduced senior staff time on routine work
This doesn’t just make it easier to access your data, but also empowers business users to carry out complex data discovery. Using the generated data catalog, they can search for individual records, research trends, and determine how to access critical information.
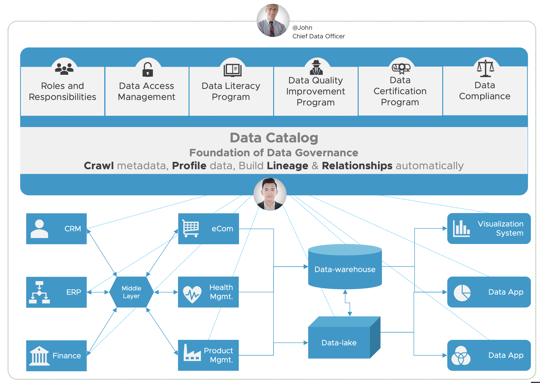
Making this data easier to access and understand also improves data literacy across your company. As Harvard Business Review reported in 2021, this is a huge problem for many businesses:
Ninety percent of business leaders cite data literacy as key to company success, but only 25% of workers feel confident in their data skills.
By giving people easier access to data using data governance, you will steadily improve data literacy across your organization. It also makes it much simpler to develop data standards and communicate these standards company-wide.
Use Case 4: Create a Centralized Repository of Standardized Business Terms
The Challenge
Lack of common language destroys data trust and creates chaos. When different teams use different definitions for the same concept, analysis becomes impossible and decisions fail.
Real-world disaster example: In 2022, Elon Musk's attempted Twitter acquisition nearly collapsed because parties couldn't agree on the definition of a "fake" account. This data governance failure cost both sides millions in legal fees and created months of uncertainty.
Common definition conflicts:
- "Active Customer": Marketing counts anyone who clicked an email in 6 months. Sales counts only those who purchased in 3 months. Finance uses 12-month purchase window. Three different metrics, three different reports, zero alignment.
- "Revenue": Product team counts committed contracts. Finance counts recognized revenue per GAAP. Sales counts closed deals regardless of payment. Leadership gets three conflicting revenue numbers.
- "Data Quality": IT measures completeness. Business measures accuracy. Compliance measures timeliness. No shared understanding of whether data is "good."
This isn't just annoying - it's expensive. Teams make wrong decisions based on misunderstood data. Projects fail because requirements were interpreted differently. Compliance audits find gaps because definitions don't match regulatory expectations.
How Data Governance Creates Shared Language
A governed business glossary provides the single source of truth for terminology across the entire organization.
Business Glossary Components:
- Standardized Definitions
- Clear, authoritative definition for every business term
- Written in business language, not technical jargon
- Approved by data governance council or domain stewards
- Includes examples and non-examples for clarity
- Lists synonyms and deprecated terms
- Data Linkage
- Connects business terms to actual data fields in systems
- Shows where each term appears: databases, reports, dashboards
- Maps terms across different systems (e.g., "Customer ID" in CRM vs. "Client Number" in ERP)
- Enables impact analysis: What breaks if we change this definition?
- Governance Workflow
- Steward assigned for each business domain
- Approval process for new terms or definition changes
- Version control tracks definition evolution over time
- Notification system alerts users when definitions change
- Dispute resolution process for conflicting opinions
- Usage Guidance
- When to use this term vs. similar terms
- Common misuses and how to avoid them
- Regulatory or compliance requirements for the term
- Best practices from successful implementations
For example, Elon Musk’s attempted Twitter acquisition recently was shrouded in controversy, as neither party could agree on the definition of a ‘fake’ account.
Real Example: Healthcare Provider Aligns Clinical and Financial Data
Challenge: A multi-hospital healthcare network with 15,000+ staff struggled with conflicting definitions between clinical and financial teams. "Patient visit" meant different things to doctors (any patient interaction), billing (reimbursable encounter), and operations (facility usage). This caused:
- Billing errors costing $2.3M annually in claim denials
- Incorrect capacity planning leading to over/understaffing
- Inaccurate reporting to regulators and board
- Physician frustration with contradictory metrics
Solution: The network implemented a governed business glossary with OvalEdge:
- Defined 300+ core healthcare terms with clinical and financial stakeholders
- Linked terms to actual fields in EHR, billing, and scheduling systems
- Established stewards for clinical, financial, and operational domains
- Built approval workflows requiring sign-off from all affected parties
- Created term relationship maps showing dependencies
Results:
- 98% of staff now use standardized definitions (up from 30%)
- Billing claim denials reduced by 75%, recovering $1.7M annually
- Capacity planning accuracy improved 40%, optimizing staffing levels
- Regulatory report preparation time cut from 3 weeks to 3 days
- Physician satisfaction with data increased 60% (reduced frustration)
- Single source of truth resolved 95% of data disputes within organization
Once your data governance tool has generated your data catalog, it’s easy to build a business glossary that everyone can access. This will include things like:
- Terms and definitions
- Data classification
- Reference data
- Technical metadata
Once this is done, you can share the glossary across the company, and continue updating it as the business evolves and grows.
A Michigan-based healthcare provider successfully grew its business by acquiring and merging with other companies, but quickly realized this had created a problem. Business terms were being used inconsistently, which made it hard for everyone to communicate.
Using OvalEdge, they were able to solve this by building a business glossary of standardized terminology, giving the whole company access. This has helped them communicate more effectively and make better business decisions.
Related: Building a Business Glossary - Why and How
Use Case 5: Centralized Data Access Management
The Challenge
The Access Management Dilemma:
Data stored everywhere? Hard to control who sees what. Data stored in one place? Complex permission management. Either way, organizations risk:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive customer data and intellectual property
- Compliance violations leading to GDPR, HIPAA, SOX fines
- Failed audits from incomplete or inaccurate access logs
- Customer trust loss from privacy breaches and data misuse
- Insider threats from overly broad permissions
According to research, 70% of employees retain access to data they no longer need, creating security vulnerabilities. Manual permission management doesn't scale - by the time IT approves access requests, business needs have changed.
Yet overly restrictive access kills productivity. If teams can't access the data they need, analysis stops, decisions get delayed, and opportunities are missed.
How Data Governance Solves Access Management
Effective data access governance provides centralized control without creating bottlenecks, balancing security with productivity.
4 Access Management Capabilities:
- Centralized Policy Management
- Define access rules once, enforce everywhere automatically
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Permissions based on job function
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC): Dynamic rules based on data sensitivity, user location, time
- Data classification drives access (Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted)
- Policies sync automatically to all connected systems
- Automated Access Workflows
- Business users request access through self-service portal
- Requests automatically routed to data owners for approval
- Time-bound access: Temporary permissions for projects
- Just-in-time access: Activate permissions only when needed
- Recertification campaigns: Quarterly review of who has access to what
- Fine-Grained Controls
- Table-level permissions for datasets
- Column-level masking for sensitive fields (show XXX-XX-1234 instead of full SSN)
- Row-level security: Users see only their department's data, region's customers, etc.
- Dynamic data masking: Hide PII in non-production environments
- Query monitoring: Detect unusual data access patterns
- Comprehensive Audit Trail
- Every data access logged: who, what, when, where, how
- Track access requests, approvals, denials, revocations
- Monitor privileged user activity (admins, DBAs)
- Generate compliance reports for auditors
- Alert on suspicious access patterns (bulk downloads, after-hours access)
Why This Matters for Compliance
Regulators require proof of data access controls:
- GDPR: "Appropriate technical and organizational measures" for data protection
- HIPAA: Minimum necessary standard - users access only data needed for job
- SOX: Separation of duties and access controls for financial data
- PCI DSS: Restrict access to cardholder data by business need-to-know
Without centralized governance, proving compliance is impossible. With it, generating audit reports takes minutes instead of weeks.
Implementation Best Practices
Start with Data Classification: You can't secure what you don't understand. Classify data by sensitivity before implementing access controls.
Define Roles Carefully: Too many roles create confusion. Too few create overly broad access. Aim for 10-15 core roles mapped to job functions.
Enable Self-Service with Guardrails: Let users request access themselves, but require data owner approval for sensitive data.
Automate Recertification: Quarterly campaigns ask managers: "Should these people still have this access?" Automation prevents access creep.
Monitor and Alert: Log everything, but alert only on high-risk patterns to avoid alarm fatigue.
Related: Data Access Management Basics & Implementation Strategy
For example, a large accounting firm needed to store financial data for companies spanning more than 34 countries. The challenge is that every country has its own tax laws and regulations.
If their audits returned results from the wrong country, it would cause big issues for the accounting firm and their customers.
Instead, they used OvalEdge for their data access management to mitigate this risk, and can manage their thousands of clients with peace of mind.
Traditional vs. Modern Data Governance Approaches
Understanding how data governance has evolved helps organizations avoid outdated practices.
|
Aspect |
Traditional Governance |
Modern Governance (2026) |
|
Approach |
Top-down, IT-led, control-focused |
Collaborative, business-driven, enablement-focused |
|
Implementation |
12-18 months waterfall projects |
6-8 weeks to first wins, agile iterations |
|
Data Discovery |
Manual, SQL queries required |
Automated catalog, self-service |
|
Policy Enforcement |
Manual audits, quarterly reviews |
Automated workflows, real-time alerts |
|
Scalability |
Limited, labor-intensive maintenance |
Scales with automation and AI assistance |
|
User Experience |
Complex, technical interfaces |
Intuitive, business-friendly UX |
|
Compliance |
Reactive, audit-driven |
Proactive, continuous compliance |
|
Data Types |
Structured databases only |
All data: structured, unstructured, streaming |
|
Cost Model |
High upfront, ongoing labor costs |
Platform investment, low maintenance |
|
AI/ML Support |
Not considered |
Built-in governance for models and training data |
The 2026 Reality: Modern governance platforms like OvalEdge enable business-led governance with automated enforcement, reducing time-to-value from 12+ months to 6-8 weeks for initial use cases.
Need help convincing stakeholders of the importance of data governance? Download our free Data Governance Business Case Builder
FAQs
1. What are data governance use cases?
Data governance use cases are practical applications where governance frameworks solve specific business challenges. Common use cases include ensuring regulatory compliance with GDPR and CCPA, improving data quality and accuracy, managing master data for a single source of truth, enabling AI and ML initiatives with trusted data, and creating business glossaries for standardized terminology.
Each use case addresses a specific pain point where ungoverned data creates compliance risk, operational inefficiency, or poor decision-making that impacts business outcomes.
2. What are the most important data governance use cases for my organization?
Priority depends on your industry, regulatory environment, and business maturity.
-
For regulated industries (healthcare, financial services): Privacy compliance and access management are critical to avoid fines.
-
For data-intensive businesses (tech, e-commerce): Data quality and self-service analytics drive competitive advantage.
-
For organizations implementing AI: AI/ML governance and data lineage are essential.
Start by assessing:
-
Where are your biggest risks?
-
Where is poor data governance causing the most pain?
-
Which use case would deliver the fastest ROI?
3. How does data governance support regulatory compliance?
Data governance enables compliance by classifying sensitive data (PII, PHI), implementing automated access controls and encryption, tracking data lineage for regulatory audits, enforcing data retention and deletion policies, and documenting consent management for privacy laws.
This creates auditable proof of compliance with GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), HIPAA (healthcare), and other regulations. Without governance, proving compliance is nearly impossible. With it, generating audit reports takes minutes instead of weeks, and violation risk drops by 90%+.
4. What is the difference between data governance and data management?
Data governance sets the strategy, policies, and standards for the "what" and "why." It defines who owns data, establishes quality standards, sets access rules, and creates the framework for data stewardship. Data management handles tactical execution, the "how."
It implements governance rules through tools, processes, and day-to-day operations like data integration, quality checks, and backup procedures. Think of it this way: Governance creates the playbook, management runs the plays. Both are necessary; neither is sufficient alone.
5. How much does data governance cost to implement?
Costs vary significantly by organization size:
-
Small businesses: $20,000-$60,000 for foundational governance (platform + basic implementation).
-
Mid-size companies: $75,000-$200,000 for enterprise-wide implementation across departments.
-
Large enterprises: $200,000-$500,000+ for complex, multi-domain governance with advanced capabilities.
This includes software platform, professional services, and internal resource time. However, ROI typically realizes within 8-12 months through reduced compliance risks (avoiding $500K-$5M+ fines), operational efficiency (40-60% faster data tasks), and improved decision-making.
6. What tools are used for data governance?
Modern data governance platforms provide comprehensive capabilities in unified solutions:
-
OvalEdge offers data catalog, governance workflows, lineage tracking, quality management, and business glossary with strong focus on usability and quick time-to-value.
-
Alternatives include: Collibra (enterprise-scale governance), Alation (data catalog-first approach), Informatica (integration-heavy solutions), and Atlan (modern data stack focus).
Choose based on your data stack complexity, organizational scale, primary use cases (compliance vs. analytics vs. AI), and whether you need unified platform or best-of-breed tools. Modern platforms like OvalEdge integrate with existing data infrastructure (databases, warehouses, BI tools) rather than replacing them.
7. How long does it take to implement data governance?
Timeline depends on scope and approach:
-
Quick wins (data catalog, basic policies): 6-8 weeks to demonstrate value.
-
Foundational governance (policies, stewardship, 1-2 domains): 3-6 months for solid foundation.
-
Enterprise-wide maturity (all domains, advanced capabilities): 12-18 months for full maturity.
Modern tools like OvalEdge use agile implementation — deliver value in weeks, then expand iteratively. Avoid "big bang" approaches that take 12+ months before delivering any value; they fail 80% of the time according to Gartner. Start with your most painful use case (usually compliance or access management), prove ROI, then expand.
8. What are the benefits of data governance?
Key benefits span multiple dimensions:
-
Compliance: 90%+ reduction in violation risk, 75-90% faster audit preparation (weeks to days), avoid multimillion-dollar fines.
-
Efficiency: 50-70% improvement in data discovery time, 40-60% reduction in data preparation effort, democratized self-service analytics.
-
Quality: 60-80% reduction in data errors, single source of truth eliminates conflicting reports.
-
Security: 60-85% lower data breach risk, comprehensive audit trails, automated access controls.
-
AI Enablement: Trusted data for model training, bias detection, explainability through lineage.
-
ROI: Average 337% over 3 years (Forrester), payback typically 8-12 months.
9. Who should own data governance in an organization?
Effective governance requires multiple roles working together:
-
Chief Data Officer (CDO) or senior executive provides strategic leadership, budget authority, and cross-functional influence.
-
Data Governance Council sets enterprise policies, prioritizes initiatives, and resolves disputes — includes business and IT leaders.
-
Data Stewards ensure quality and policy compliance in their domains (Customer Data, Product Data, Financial Data) — typically 20-40% role for domain experts.
-
Data Owners (business leaders) make decisions about their data and approve access requests.
-
Data Custodians (IT/engineers) handle technical implementation and platform management.
Critical success factor: Business must co-own governance with IT. IT-only governance initiatives fail 80% of the time because they lack business context and stakeholder buy-in.
10. How do you measure data governance success?
Track both leading indicators (predict future success) and lagging indicators (measure outcomes):
-
Leading Indicators: Percent of data assets cataloged and governed (target: 70-85% of critical data within 6 months), data quality scores trending upward, policy compliance rates, user adoption of self-service tools.
-
Lagging Indicators: Compliance audit pass rate and preparation time (weeks to days reduction), data quality error reduction (60-80% improvement), time to insights for analytics (50-70% faster), policy violation count (downward trend), user satisfaction scores (quarterly surveys).
-
Business Outcomes: Revenue enabled through data-driven decisions, cost savings from efficiency gains, risks avoided (compliance fines, breaches).
Establish baseline metrics before implementation, then track monthly. Communicate wins to stakeholders to maintain momentum and support.
11. What is master data management (MDM) in data governance?
Master data management creates a single, authoritative source of truth for critical business entities like customers, products, suppliers, locations, and employees. It works by:
-
Consolidating data from multiple source systems into one golden record.
-
Eliminating duplicates through sophisticated matching algorithms.
-
Ensuring consistency through governance rules and quality checks.
-
Synchronizing changes back to source systems bidirectionally.
Governance role: MDM without governance fails because no one agrees on rules for merging records, resolving conflicts, or defining what "golden" means. Governance provides: data stewardship (who decides), data quality standards (accuracy rules), policies for match/merge, and workflow for exceptions. MDM enables accurate reporting, 360-degree views (customer, product), improved analytics, and operational efficiency.
12. How does data governance enable AI and machine learning?
AI and ML require high-quality, well-understood, bias-free data — exactly what governance provides:
-
Training Data Quality: Governance ensures completeness (no missing values), accuracy (correct labels), consistency (definitions align), and timeliness (data is current). Poor quality training data causes hallucinations and unreliable predictions.
-
Bias Detection: Governance identifies underrepresented groups in datasets, tests for algorithmic bias (gender, race, age), documents mitigation steps, and tracks fairness metrics.
-
Explainability: Data lineage shows which data influenced model decisions, enables "right to explanation" for AI decisions, and helps debug model errors by tracing data provenance.
-
Feature Store Governance: Catalogs ML features with business definitions, controls access to sensitive features, versions features to ensure reproducibility.
Critical stat: 80% of AI projects fail due to poor data governance (Gartner 2024). Without trusted, governed data, AI initiatives waste millions and deliver poor results.
Book a call with us to find out:
|
Deep-dive whitepapers on modern data governance and agentic analytics

OvalEdge recognized as a leader in data governance solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.



