Table of Contents
How to Implement Data Governance in Small and Mid-Sized Banks
Data governance is crucial in every industry, but the stringent regulatory requirements in the financial sector make well-governed data one of the highest business-critical priorities. Globally, banks are required to abide by specific regulatory practices, and these requirements are stringent.
Ultimately, banking regulations are tailored to the amount a bank has in assets. Fundamentally, this is because smaller banks deal with banking activities, like loans and deposits, that have less of a potential impact on the broader economic climate of a jurisdiction than larger banks that deal with securities.
Comprehensive data governance is critical, no matter how big or small your bank is. However, when a US bank exceeds $10 billion in assets, the requirements from regulators ramp up considerably. Despite being eased by the 2018 Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act; the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 laid out strict regulatory policies for banks breaching $10 billion in assets, many of which still stand.
Related Post: Risk Assessment in Banking
Let’s break down how small and mid-sized banks can implement effective data governance programs that ensure compliance, strengthen data security, and drive better business decisions. Read on to learn more.
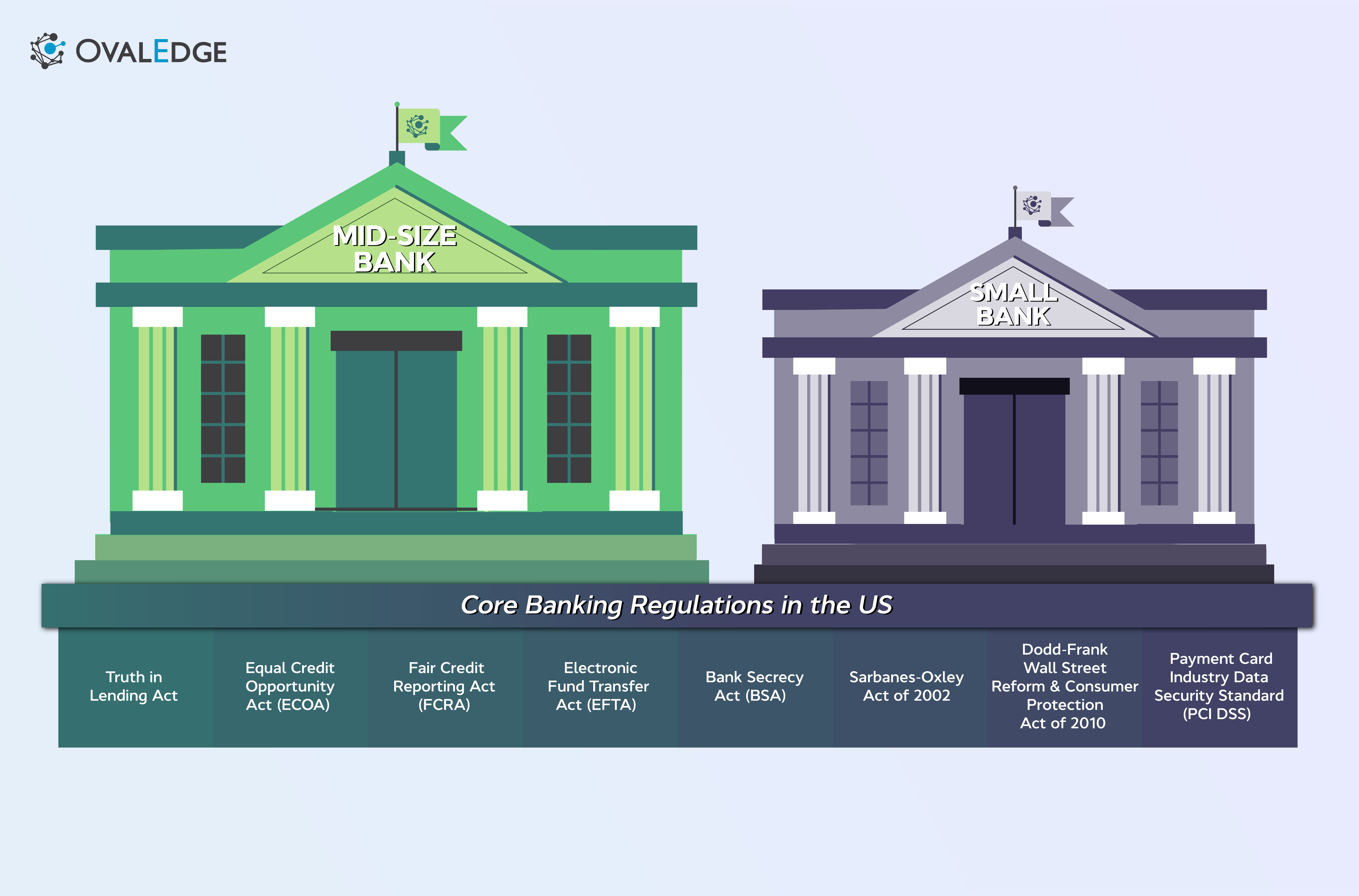
What are the core banking regulations in the US?
Small to mid-sized banks must be aware of a comprehensive range of banking regulations that, while different, all carry significant penalties for non-compliance. They include the following:
- The Truth in Lending Act demands that lenders disclose comprehensive details about loan terms and the cost to borrowers.
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) is in place to ensure that banks don't follow discriminatory practices when deciding who to lend to.
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) protects customers' credit information, ensures access to credit scores, and allows them to make amendments when something is wrong.
- The Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA) covers electronic banking transactions, like debit cards, ATMs, and online banking activities.
- The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) requires banks to implement anti-money laundering procedures.
- The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 is one of the best-known regulations focusing on corporate governance and transparent financial reporting.
- The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 aims to reduce risk in the financial industry and protect consumers from malpractice.
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) governs the safe and secure processing and storage of consumer cardholder information.
Common Data Governance Challenges in Banking
Hurdles are inevitable when implementing data governance in banking. These challenges range from technical and regulatory to organizational and cultural barriers.
1. Data Complexity and Volume
Banks process massive amounts of customer, transaction, and market data daily. Managing this data’s accuracy, timeliness, and consistency can be overwhelming.
2. Data Silos
Disparate systems across departments create data silos, making unified visibility and analytics difficult.
3. Data Security
Banks are prime targets for cyberattacks. Balancing strong data protection with authorized user access requires careful governance.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Complying with evolving frameworks like Dodd-Frank, Basel III, and GDPR demands meticulous data documentation and traceability.
5. Data Privacy
Protecting sensitive customer data with encryption, anonymization, and consent management is critical.
6. Legacy Systems
Older core banking platforms often lack modern data governance integration capabilities.
7. Change Management
Effective governance requires a cultural shift. Resistance from teams unfamiliar with governance workflows can slow adoption.
8. Data Quality
Duplicate, inconsistent, or missing data can undermine compliance and analytics accuracy.
9. Governance Framework Definition
Defining a data governance framework aligned with business goals and regulations can be challenging.
10. Training & Awareness
Educating staff on data ownership and governance best practices requires ongoing effort.
11. Measuring Success
Tracking KPIs to measure governance effectiveness—like data quality scores or compliance breach reductions—can be complex.
12. Cloud Migration
As banks adopt cloud infrastructure, extending governance policies securely to hybrid or multi-cloud setups is essential.
🧭 Tackling these challenges requires leadership commitment, cross-team collaboration, and a governance platform like OvalEdge to streamline compliance and data control.
How to develop a data governance program?
Modern data governance implementation doesn’t need to be complex or expensive. Thanks to platforms like OvalEdge, small banks can now build effective governance frameworks incrementally.
Step 1: Build Your Governance Team
- Appoint a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or governance lead.
- Identify stakeholders from compliance, risk, IT, and business units.
- Combine one full-time data governance role with department-level “data champions.”
Step 2: Define Governance Policies
- Establish policies for data privacy, access, and quality.
- Ensure alignment with frameworks like Dodd-Frank, compliance data governance, and PCI DSS.
- Define escalation procedures for policy breaches.
Step 3: Improve Data Literacy
Enable every employee to access and interpret governed data.
A strong data culture promotes smarter decisions and accountability.
Step 4: Enhance Data Quality
Implement continuous data profiling, cleansing, and enrichment programs to ensure your data is accurate and reliable.
Step 5: Strengthen Privacy and Access Controls
Use AI-powered classification to detect PII and enforce role-based access controls (RBAC).
Step 6: Use Automated Lineage Building
Map where data originates, flows, and is used for audit trails and compliance reporting.
Step 7: Leverage a Self-Service Data Governance Tool (like OvalEdge)
OvalEdge helps:
- Crawl metadata and build a central catalog.
- Automate access management and privacy rules.
- Enable self-service analytics for business users.
What are the broader benefits of data governance?
Of course, compliance is the primary driver for data governance in the banking sector, but it isn't the only one. When data is of high quality, one of the consequences of data governance and a requirement when preparing it for compliance, it can be used as a strategic asset. Strong data governance for small banks not only meets compliance but also boosts performance and innovation.
Related Post: Implementing Data Quality for Fair Lending Compliance in Banking
As AI matures, more new technologies will help you add value to your data. For example, you might find a better AI-powered credit scoring program and make data-driven decisions more quickly. However, these mechanisms need high-quality data to run efficiently.
Before, when you wanted a technology, purchasing it was a simple process. However, an extensive dividing line enabled banks with large budgets to get the competitive edge because of the high price many of these technologies demanded. Today, the playing field is more level, but there is a caveat: the technology runs on your data. So, if your data is of low quality, you won't be able to leverage the technology sufficiently, and your competitors will take advantage.
Competition is based on operational efficiency, which depends on today's technologies. While everybody has access to the same technology, banks with comprehensive data governance in place will have a competitive advantage because they can dramatically reduce time to market.
How to implement data governance with OvalEdge
Lineage building is the core process in preparing data for compliance in the banking industry. This was a costly undertaking, but with a data governance tool like OvalEdge, the same task can be carried out at a much lower cost.
With OvalEdge, users crawl all the metadata and collate this knowledge into a centralized data catalog. From here, along with lineage building, you can implement a series of data governance programs that constitute end-to-end governance in your organization.
1. Data literacy
Ensure that everyone in your organization has governed access to data via self-service. This helps users learn how to use data to develop new strategies, collaborate on projects, and drive a culture of data-driven decision-making.
2. Data quality improvement
Make your data high-quality and actionable with an ongoing data quality improvement program embedded into the OvalEdge platform.
3. Data privacy and access
Data access management features enable you to develop policies that can be implemented automatically, while ad-hoc access management enables you to grant specific access requests. Use AI algorithms to identify and classify PII and other sensitive data, and use this knowledge to allow secure access to verified users.
FAQs
1. What are key data governance regulations for banks?
Banks must comply with Dodd-Frank, GDPR, Basel III, PCI DSS, and BSA regulations to manage risk and ensure transparency.
2. How does OvalEdge help with banking compliance?
OvalEdge automates metadata management, lineage tracking, and access control, helping banks simplify compliance audits and improve data trust.
3. What’s included in a data governance program in banking?
A governance program includes policies for data access, privacy, quality, and regulatory compliance, all monitored continuously.
Book a call with us to find out:
|
Deep-dive whitepapers on modern data governance and agentic analytics

OvalEdge recognized as a leader in data governance solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.


