Table of Contents
Data Lineage Guide: Examples, Benefits & Implementation
QUICK ANSWER
Data lineage is the process of tracking and visualizing the flow of data from its origin to its destination, including all transformations and changes along the way. It provides transparency into where data comes from, how it changes, and where it's used across your organization's systems.
This article aims to demystify the intricacies of data lineage by exploring its two main types, Business Data Lineage and Technical/ETL Data Lineage, with clear examples illustrating their practical applications. As we delve into the realms of business processes and technical intricacies, the importance of data lineage will become apparent in fostering transparency, ensuring data quality, and empowering organizations to make informed decisions.
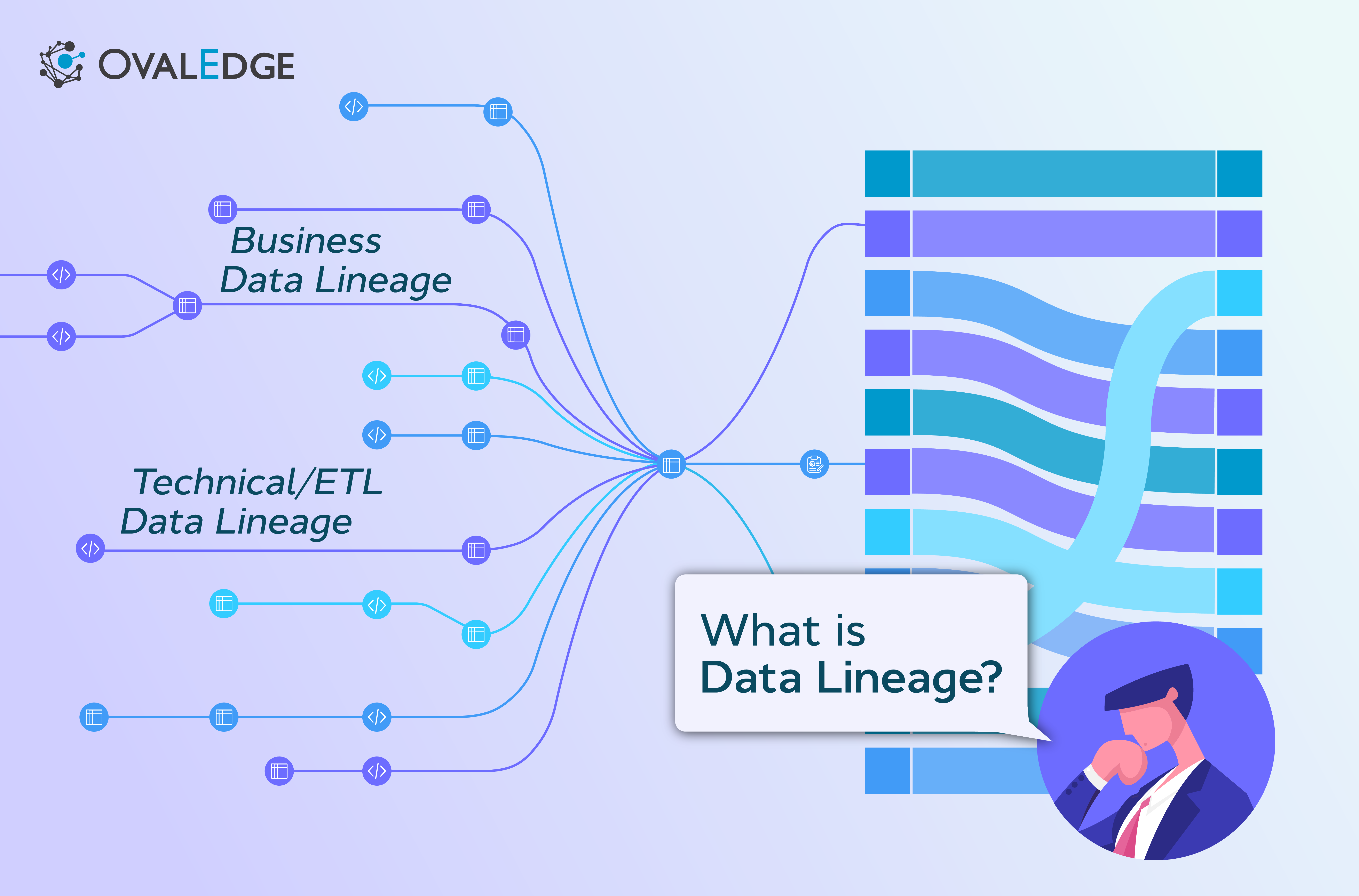
What is Data Lineage?
Data lineage is a critical aspect of data management that visually represents the flow and transformation of data throughout its lifecycle. It offers transparency into the origins, movements, and transformations of data within an organization's systems and business processes.
By tracing the journey of data, organizations can enhance data quality, ensure regulatory compliance, build trust in data, and make more informed decisions. Think of data lineage as a detailed map showing not just where your data is, but the complete story of how it got there.
In today's complex data environments with data flowing through multiple systems, undergoing various transformations, and being consumed by numerous applications, understanding data lineage has become essential for maintaining data integrity and meeting compliance requirements.
Two Types of Data Lineage
Data lineage encompasses two main types: Business Data Lineage and Technical/Operational/ETL Data Lineage, each serving distinct purposes in understanding and managing data flow within an organization.
Business Data Lineage
Business Data Lineage delves into the ways various business processes interact with and utilize data. It seeks to answer critical questions about the business's data ecosystem:
Data Consumption by Business Processes:
- Explore how different business processes consume and interact with the data
- Identify the touchpoints where data is input, transformed, or output within business operations
- Understand which departments and teams rely on specific data assets
Data Representation in Business Activities:
- Understand which business activities or processes are represented by the data
- Clarify the role of the data in supporting specific business functions
- Map data assets to business outcomes and KPIs
Terminology and Definitions:
- Define the terms and concepts used within the data to ensure a shared understanding across the organization
- Establish a standardized vocabulary to enhance communication and collaboration
- Create a common language between technical and business teams
Data Utilization for Reporting and Decision-Making:
- Investigate how the data contributes to generating reports
- Analyze the role of the data in supporting decision-making processes within the organization
- Track which executives and teams depend on specific data for strategic decisions
Related Post: The Top Features of a Comprehensive Data Catalog
Example of Business Data Lineage
Consider a retail company tracking its revenue, where the calculation involves three types of sales:
- Product sales at point of sale - This revenue is directly sourced from the point of sale reporting system.
- Advertising revenue - This revenue is generated by leasing space for various advertisements. This revenue figure is extracted directly from a spreadsheet the advertising team manages.
- Rental revenue - This is obtained from leasing spaces to businesses like restaurants or hair salons and can be sourced from the leasing software, a spreadsheet, or directly from the invoicing system.
Tracking the entire process outlined above constitutes business lineage. This lineage should include information on who updates the spreadsheet, the individuals with access permissions, the timing of updates, and whether updates occur post-invoicing or after collecting payment.
Technical / Operational / ETL Data Lineage
This type of data lineage focuses on the technical aspects of data movement and processing within systems. It aims to provide a detailed understanding of the operational journey of data:
Data Movement Across Systems:
- Trace how data moves from one system to another throughout the entire data pipeline
- Identify the integration points and mechanisms used for data transfer
- Document APIs, file transfers, and database connections
Data Processing Details:
- Uncover the specifics of what happens to the data during each processing step
- Examine transformations, cleansing, and any modifications made to the data
- Track calculations, aggregations, and data enrichment activities
Error and Anomaly Detection:
- Investigate whether there were any errors or anomalies encountered during data processing
- Implement measures to monitor and rectify issues that may arise
- Create alerts for data quality violations
Timing and Performance Analysis:
- Analyze the timing and performance metrics of each step in the data pipeline
- Optimize processing steps to improve efficiency and reduce latency
- Identify bottlenecks and resource constraints
Related Post: Top 8 Features of a Data Quality Tool
Example of Technical Lineage
In the retail company, when tracking revenue, data is sourced from three systems:
- Point of Sale Reporting System
- Excel Sheet
- Leasing Software
Technical lineage monitors the flow of data from these three distinct software platforms into the data warehouse. Subsequently, it traces the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process, which involves a formulaic calculation.
This calculation may include summing the daily point-of-sale figures for the year 2023 and adding the yearly revenue from the Excel Sheet. The finalized data is then directed to a dashboard created in either Tableau or Power BI.
Business vs Technical Lineage: Quick Comparison
|
Aspect |
Business Lineage |
Technical Lineage |
|
Focus |
Business processes and meaning |
Technical systems and data flow |
|
Users |
Business analysts, executives, and compliance teams |
Data engineers, IT teams, developers |
|
Questions Answered |
"What does this data mean?" "Who uses it?" |
"Where does this data come from?" "How is it transformed?" |
|
Granularity |
High-level business concepts |
Detailed technical specifications |
|
Examples |
Revenue calculation process, customer journey |
ETL jobs, database queries, API calls |
Key Benefits of Data Lineage
Understanding data lineage provides numerous advantages that directly impact data quality, compliance, and operational efficiency. Here are the primary benefits:
1. Enhanced Data Quality and Trust
Data lineage helps organizations identify and fix data quality issues at their source. When you can trace data back to its origin and see every transformation it undergoes, you can quickly spot where errors creep in. This transparency builds trust in your data, making teams more confident in using it for critical decisions.
For instance, if a financial report shows unexpected numbers, lineage allows you to trace back through each calculation and transformation to find the exact point where the error occurred, whether it's a faulty ETL process, an incorrect formula, or bad source data.
Learn more: AI-Powered Open Source Data Quality Tools
2. Regulatory Compliance and Audit Support
In today's regulatory environment, organizations must demonstrate how they handle data, especially sensitive information like personally identifiable information (PII) or protected health information (PHI).
Data lineage provides automatic audit trails that show:
- Where sensitive data originates
- How it's transformed and used
- Where it's stored
- When it's deleted
This documentation is essential for compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and SOX. When auditors ask, "How do you handle customer data?" you can provide visual diagrams showing the complete journey.
Related: Data Governance & Compliance Framework
3. Faster Root Cause Analysis and Impact Assessment
When data issues occur will lineage dramatically reduces troubleshooting time. Instead of spending days manually tracing through systems and asking colleagues, you can visualize the entire data flow in minutes.
Similarly, when you need to make changes to your data infrastructure, lineage shows you exactly what will be affected. Before modifying a database table, you can see every downstream report, dashboard, and process that depends on it, preventing unexpected breakages.
4. Efficient Data Migration and System Changes
Migrating to the cloud or upgrading systems becomes significantly easier with comprehensive lineage. You can:
- Identify all dependencies before starting
- Prioritize migrations based on data criticality
- Validate that the migrated data maintains the same transformations
- Test downstream impacts before going live
Organizations with strong lineage documentation complete migrations 30-50% faster than those without it.
5. Improved Collaboration Between Teams
Data lineage creates a shared language between technical and business teams. Data engineers can see how their technical work impacts business metrics, while business users gain visibility into the technical underpinnings of their reports.
This transparency enables better collaboration on data governance initiatives, making it easier to establish ownership, set quality standards, and implement policies.
Common Use Cases for Data Lineage
Data lineage serves multiple practical purposes across different organizational functions. Here are the most common scenarios where lineage proves invaluable:
Use Case 1: Impact Analysis for Changes
The Scenario: Your team needs to modify a source database table that's been around for years. You're not sure what might break if you change it.
How Lineage Helps: Lineage shows you every ETL job, report, dashboard, and application that depends on that table. You can see:
- Which columns are actually used downstream
- What transformations rely on specific data types
- Which business-critical reports might be affected
- Who needs to be notified about the change
The Result: Instead of making the change and hoping nothing breaks, you can proactively identify and test all impacted systems, communicate with affected stakeholders, and implement the change confidently.
Use Case 2: Data Quality Troubleshooting
The Scenario: Your executive dashboard shows revenue numbers that don't match expectations. The finance team is asking questions, and you need answers quickly.
How Lineage Helps: Starting from the problematic metric, you can trace backwards through:
- The BI tool calculations
- The data warehouse aggregations
- The ETL transformations
- The source system data
The Result: You identify that a recent change to the ETL logic inadvertently excluded a revenue category. What could have taken days of investigation takes minutes, and you can quickly fix the issue.
Use Case 3: Regulatory Compliance Documentation
The Scenario: You need to demonstrate GDPR compliance for how you handle customer personal data across your entire organization.
How Lineage Helps: Lineage provides automatic documentation showing:
- Every system where personal data is stored
- How personal data flows between systems
- What transformations are applied
- How long data is retained
- How data is eventually deleted
The Result: You can generate compliance reports automatically, respond to auditor questions with visual documentation, and demonstrate full control over personal data throughout its lifecycle.
Related: Data Governance in Banking
Use Case 4: Cloud Migration Planning
The Scenario: You're migrating your data warehouse from on-premises to the cloud and need to understand all the dependencies.
How Lineage Helps: Lineage maps:
- All source systems feeding your data warehouse
- Every ETL job that needs to be recreated or modified
- All downstream systems consuming warehouse data
- Legacy connections that might need updating
The Result: You can create a comprehensive migration plan, identify potential issues before they occur, and ensure no critical connections are forgotten.
Use Case 5: Data Product Development
The Scenario: You're building a new data product (like a customer 360 view or machine learning model) and need to understand what data is available and trustworthy.
How Lineage Helps: Lineage shows you:
- Which data sources are most current and complete
- How different data assets relate to each other
- Which transformations might affect data quality
- What similar data products already exist
The Result: You can avoid duplicating effort, build on existing data pipelines, and ensure your new product uses high-quality, well-understood data.
Learn more: Measuring AI Readiness
Use Case 6: Vendor System Integration
The Scenario: You're integrating a new SaaS tool into your data ecosystem and need to ensure it doesn't disrupt existing processes.
How Lineage Helps: Lineage reveals:
- Potential data conflicts with existing systems
- Opportunities to consolidate duplicate data flows
- Dependencies that the new tool might affect
- Integration points that need special attention
The Result: The integration proceeds smoothly because you've identified and addressed potential issues before they impact production systems.
Data Lineage Techniques and Approaches
Organizations can capture and maintain data lineage through several technical approaches, each with its own advantages and use cases:
1. Parsing-Based Lineage
How it works: Automated tools analyze your SQL code, ETL scripts, and transformation logic to extract lineage relationships. The tools read through your codebase and build the lineage graph automatically.
Best for: Organizations with well-documented code and standardized ETL processes. Works particularly well for SQL-heavy environments.
Pros:
- Highly accurate for supported code types
- Automatic updates as code changes
- Minimal manual effort required
Cons:
- May struggle with dynamic SQL or complex stored procedures
- Requires tool support for your specific technologies
- Initial setup can be complex
Popular Tools: OvalEdge, Collibra, Informatica
Learn more: Data Lineage Techniques
2. Metadata-Based Lineage
How it works: Systems track lineage by capturing and analyzing metadata from your data infrastructure. This includes database logs, ETL job logs, and API calls.
Best for: Large enterprises with diverse technology stacks where not all code is accessible for parsing.
Pros:
- Works across heterogeneous systems
- Can capture runtime behavior, not just code
- Handles black-box transformations
Cons:
- May be less detailed than parsing
- Requires metadata collection infrastructure
- Can miss manual or ad-hoc processes
Popular Tools: Apache Atlas, Marquez, OpenLineage
3. Tagging-Based Lineage
How it works: Data elements are tagged as they move through your systems, creating a trail that can be followed to reconstruct lineage.
Best for: Real-time data pipelines and streaming architectures where traditional parsing is difficult.
Pros:
- Works well for streaming data
- Can track data through microservices
- Captures actual runtime flow
Cons:
- Requires code changes to implement tagging
- Overhead on data processing
- May miss transformations that don't preserve tags
Popular Tools: OpenLineage (with instrumentation), custom solutions
4. Pattern-Based Lineage
How it works: The system identifies common patterns in how data flows and applies those patterns to infer lineage relationships.
Best for: Organizations just starting with lineage who need quick wins without extensive tool investment.
Pros:
- Fast to implement for common patterns
- Requires less technical infrastructure
- Good for initial lineage documentation
Cons:
- Less accurate than parsing or metadata
- Requires pattern maintenance
- May miss unique transformations
Best Practice: Most organizations use a combination of these techniques. Start with parsing for your core data warehouse, add metadata collection for broader coverage, and use patterns to fill gaps.
Data Lineage Levels: System, Object, and Column
Data lineage can be captured at different levels of granularity, each serving different purposes and audiences:
System-Level Lineage
What it shows: How data moves between major systems (e.g., from Salesforce to Data Warehouse to Tableau).
Who uses it: Enterprise architects, IT leadership, data governance teams
Use cases:
- High-level system architecture documentation
- Identifying system dependencies for migrations
- Understanding data flow across the organization
- Planning system upgrades or replacements
Example: "Customer data flows from our CRM system through our data warehouse and is consumed by our marketing analytics platform and customer support system."
Object-Level Lineage (Table/File Level)
What it shows: How specific tables, views, or files relate to each other.
Who uses it: Data analysts, BI developers, data engineers
Use cases:
- Understanding which tables feed specific reports
- Impact analysis for database changes
- Troubleshooting data quality issues
- Planning data model optimizations
Example: "The customer_orders table is created by joining the raw_orders and customers tables, and is used by the monthly_revenue report and the customer_churn model."
Related: Open Source Data Catalog Tools
Column-Level Lineage
What it shows: How specific columns or fields transform as data moves through systems, including the exact calculations and logic applied.
Who uses it: Data engineers, compliance officers, quality analysts
Use cases:
- Precise compliance documentation (e.g., tracking PII)
- Detailed troubleshooting of calculation errors
- Understanding complex business logic
- Validating data accuracy
Example: "The customer.email column originates from crm.contact.email_address, is standardized to lowercase in the ETL process, and appears in the marketing. subscribers.email field."
Choosing the Right Level
|
Level |
Detail |
Effort to Maintain |
Best For |
|
System |
Low |
Low |
Strategic planning, architecture |
|
Object |
Medium |
Medium |
Day-to-day development, impact analysis |
|
Column |
High |
High |
Compliance, precise troubleshooting |
Best Practice: Implement all three levels, but focus your initial efforts on object-level lineage for the best balance of usefulness and effort. Add column-level detail for compliance-critical fields and sensitive data.
How to Implement Data Lineage: A Practical Guide
Implementing data lineage doesn't have to be overwhelming. Follow this phased approach to build lineage capabilities that grow with your organization:
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (2-4 weeks)
- Identify High-Value Use Cases
Start by understanding what problems lineage will solve for your organization:
- Are you struggling with troubleshooting data issues?
- Do you face compliance requirements for data tracking?
- Are you planning a cloud migration?
- Do you need better impact analysis for changes?
Prioritize 2-3 use cases that will demonstrate clear value quickly.
- Map Your Data Landscape
Document your current state:
- Major data sources (databases, SaaS apps, files)
- Key transformation systems (ETL tools, data warehouses)
- Primary consumers (BI tools, applications, reports)
- Critical data flows that support business operations
You don't need to map everything; focus on the most important data pipelines first.
- Select Your Approach and Tools
Based on your use cases and data landscape, choose:
- Automated lineage tool (recommended for most organizations) - OvalEdge, Collibra, Alation
- Open source solution (for technical teams with resources) - Apache Atlas, OpenLineage
- Hybrid approach (combination of automated and manual documentation)
Consider: budget, technical resources, data complexity, and timeline.
Explore: Data Governance Tool Capabilities
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (4-8 weeks)
- Start with a Critical Pipeline
Choose one important data flow to implement lineage first:
- A compliance-critical data flow (e.g., customer PII)
- A frequently troublesome pipeline
- A business-critical report or dashboard
- An upcoming migration target
- Set Up Your Tool
Configure your chosen lineage tool:
- Connect to source systems
- Configure parsers or collectors
- Set up authentication and permissions
- Test data extraction
- Validate and Refine
Work with data engineers and analysts to:
- Verify lineage accuracy
- Fill in gaps (especially for manual processes)
- Add business context and descriptions
- Test key use cases
- Demonstrate Value
Document quick wins:
- Time saved in troubleshooting
- Compliance documentation generated
- Impact assessments completed
- Stakeholder feedback
Phase 3: Expansion (3-6 months)
- Expand Coverage
Gradually add more systems and pipelines:
- Prioritize based on business value and risk
- Add new source systems incrementally
- Expand to additional data domains
- Document edge cases and exceptions
- Automate Maintenance
Reduce manual effort:
- Set up automated lineage refresh
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines
- Configure alerts for lineage staleness
- Establish regular validation processes
- Enable Self-Service
Make lineage accessible to more users:
- Provide training on how to read lineage diagrams
- Create documentation and best practices
- Set up role-based access controls
- Gather user feedback and iterate
Related: Data Governance Committee Structure
Phase 4: Maturity and Optimization (Ongoing)
- Integrate with Broader Data Governance
Connect lineage to other governance activities:
- Link to data quality monitoring
- Connect to data cataloging efforts
- Support data access management
- Enable policy enforcement
- Measure and Improve
Track key metrics:
- Lineage coverage (% of critical pipelines documented)
- Time to troubleshoot issues
- Compliance audit preparation time
- User adoption and satisfaction
- Advanced Use Cases
Leverage mature lineage for:
- Automated impact analysis in CI/CD
- ML model training data tracking
- Real-time data quality alerting
- Proactive compliance monitoring
Common Implementation Pitfalls to Avoid
❌ Trying to document everything at once - Start small, prove value, then expand
❌ Focusing only on technical lineage - Include business context for broader adoption
❌ Manual documentation without automation - Manually maintained lineage quickly becomes outdated
❌ Tool selection before use case definition - Know what problems you're solving first
❌ Lack of executive sponsorship - Get buy-in by demonstrating ROI early
✅ Start with a high-impact, manageable scope
✅ Automate capture wherever possible
✅ Include both technical and business perspectives
✅ Demonstrate quick wins to build momentum
✅ Plan for long-term maintenance from day one
Data Lineage Tools and Technologies
The data lineage tool landscape includes enterprise platforms, modern data stack tools, and open source options. Here's how to evaluate them:
Enterprise Data Governance Platforms
Examples: OvalEdge, Collibra, Alation, Informatica
Best for: Large enterprises needing comprehensive governance beyond just lineage
Key Features:
- Integrated data cataloging, quality, and lineage
- Broad connector support for diverse data sources
- Enterprise-grade security and scalability
- Professional support and training
Considerations:
- Higher cost but comprehensive features
- May include capabilities beyond lineage needs
- Typically requires some implementation effort
- Strong for regulatory compliance use cases
When to Choose: You need end-to-end data governance with lineage as one component, have a budget for enterprise tools, and require broad system coverage.
Learn more: Data Catalog Pricing Guide
Modern Data Stack Tools
Examples: Monte Carlo, Atlan, Datafold
Best for: Teams using modern cloud data stacks (Snowflake, Databricks, dbt)
Key Features:
- Native integration with modern data tools
- Focus on data observability and quality
- Developer-friendly interfaces
- Fast deployment for supported systems
Considerations:
- May have limited support for legacy systems
- Primarily technical lineage focus
- Pricing can scale quickly with data volume
- Often part of a broader observability platform
When to Choose: You're primarily on modern cloud platforms, value speed of deployment, and want observability features alongside lineage.
Explore: Data Observability Tools
Open Source Options
Examples: Apache Atlas, OpenLineage, Marquez, Amundsen
Best for: Organizations with strong technical teams and specific customization needs
Key Features:
- No licensing costs
- Full customization capability
- Active community support
- Can integrate with existing tools
Considerations:
- Requires technical resources for implementation
- Limited out-of-the-box functionality
- Maintenance and updates are your responsibility
- May need multiple tools for a complete solution
When to Choose: You have engineering resources available, need deep customization, or want to avoid vendor lock-in.
Learn more: AI-Powered Open Source Data Lineage Tools
How to Evaluate Lineage Tools
When selecting a data lineage tool, consider these critical factors:
- Coverage
- Does it support your current data platforms?
- Can it handle your planned technology additions?
- Does it capture the right level of detail (system/object/column)?
- Automation Level
- How much is automatically captured vs. manually documented?
- Does it update lineage as your code changes?
- Can it handle your specific ETL patterns and tools?
- Usability
- Can non-technical users understand the lineage visualizations?
- Is search and navigation intuitive?
- Does it provide business context alongside technical details?
- Integration
- How well does it integrate with your existing tools (BI, data catalog, etc.)?
- Can you embed lineage into existing workflows?
- Does it have APIs for custom integrations?
- Scalability
- Can it handle your data volumes?
- How does performance scale as you add more systems?
- What are the infrastructure requirements?
- Total Cost of Ownership
- License/subscription costs
- Implementation and training
- Ongoing maintenance and updates
- Infrastructure and compute resources
OvalEdge's Approach to Data Lineage
OvalEdge provides automated, end-to-end data lineage that integrates seamlessly with broader data governance:
- Automated Capture: Parses SQL, ETL code, and BI tools to auto-generate lineage down to the column level
- Broad Coverage: 150+ connectors for databases, cloud platforms, and business intelligence tools
- Business Context: Links technical lineage to business glossary terms and data quality metrics
- Impact Analysis: Visual exploration of upstream and downstream dependencies
- Compliance Support: Automated audit trails for regulatory requirements
See OvalEdge Data Lineage in Action
Related Post: What is Data Quality? Dimensions & Their Measurement
Data Lineage Best Practices
To maximize the value of your data lineage efforts, follow these proven best practices:
1. Balance Automation with Documentation
The Practice: Automate lineage capture wherever possible, but supplement with manual documentation for business context.
Why it matters: Automated tools excel at capturing technical relationships but often miss the "why" behind data flows. Business users need context about what the data means and how it should be used.
How to implement:
- Use tools to auto-capture technical lineage
- Add business descriptions to key data elements
- Document business rules and calculations in plain language
- Create glossaries linking technical and business terms
2. Maintain Multiple Lineage Views
The Practice: Provide different lineage views for different audiences.
Why it matters: Data engineers need column-level technical details, while executives need high-level business process views. A single view can't serve everyone.
How to implement:
- System-level view for architects and management
- Object-level view for analysts and developers
- Column-level view for compliance and deep troubleshooting
- Business process view for non-technical stakeholders
3. Keep Lineage Current
The Practice: Treat lineage as living documentation that updates as your data environment changes.
Why it matters: Outdated lineage is worse than no lineage; it creates false confidence and leads to incorrect decisions.
How to implement:
- Integrate lineage updates into CI/CD pipelines
- Set up automated refresh schedules
- Alert when lineage hasn't updated in a defined period
- Review and validate lineage during code reviews
4. Link Lineage to Data Quality
The Practice: Connect lineage to data quality monitoring and issue tracking.
Why it matters: When quality issues arise, lineage helps find the root cause. When lineage shows a change, quality monitoring verifies it didn't break anything.
How to implement:
- Tag quality issues with affected lineage paths
- Trigger quality checks when lineage changes
- Display quality scores alongside lineage diagrams
- Use lineage for impact analysis of quality fixes
Learn more: The Four Pillars of Data Governance
5. Establish Lineage Ownership
The Practice: Assign clear ownership for maintaining and validating lineage.
Why it matters: Without ownership, lineage documentation degrades quickly as systems change.
How to implement:
- Data owners validate lineage for their domains
- Data stewards maintain the business context
- Data engineers verify technical accuracy
- Include lineage validation in change management processes
6. Start with Critical Paths
The Practice: Prioritize lineage documentation for your most important data flows.
Why it matters: You can't document everything immediately. Focus where risk and value are highest.
How to implement:
- Map data supporting compliance requirements
- Document flows for executive dashboards
- Prioritize revenue and customer-critical data
- Cover data supporting operational decisions
- Expand gradually to less critical areas
7. Use Lineage Proactively, Not Just Reactively
The Practice: Build lineage into your development and change processes, not just for troubleshooting.
Why it matters: Proactive use prevents problems; reactive use only helps clean up after they occur.
How to implement:
- Review lineage before making schema changes
- Check the impact analysis in the code review process
- Validate lineage as part of the deployment checklist
- Use lineage in the design phase of new data products
8. Communicate Lineage Value
The Practice: Actively demonstrate and communicate the benefits of data lineage to stakeholders.
Why it matters: Lineage requires ongoing investment. Stakeholders need to see ROI to maintain support.
How to implement:
- Track and share metrics (time saved, issues prevented)
- Celebrate lineage success stories in team meetings
- Include lineage benefits in governance presentations
- Quantify compliance and audit efficiency gains
Related Post: Top Features of a Data Lineage Tool in 2024
Why do we need data lineage?
Data lineage offers several key benefits in data management and analytics:
- Improved Data Quality and Accuracy: By tracking the origin and transformations of data, data lineage helps in identifying and correcting errors. In case a data problem is at some source system, It can help you communicate with all the impacted people who might be affected.
- Enhanced Data Governance: Data lineage supports robust data governance by providing data processing and movement transparency. This is crucial for complying with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, which require detailed knowledge of data origins and transformations.
- Easier Error Identification and Resolution: When data issues arise, data lineage allows teams to quickly trace back through the data pipeline to identify where the error originated, significantly reducing the time and effort needed for troubleshooting.
- Better Impact Analysis: Understanding how changes in one part of the data system affect others is essential. Data lineage provides insights into dependencies and relationships between data elements, enabling more effective impact analysis when changes are proposed.
- Increased Trust and Confidence in Data: For decision-makers and data consumers, knowing the history and transformations of data increases confidence in its validity and suitability for use in decision-making processes.
- Efficient Data Management and Migration: When migrating data from one system to another or integrating new data sources, data lineage provides a clear map of data flows, simplifying these processes and reducing risks.
- Streamlined Regulatory Compliance: Data lineage helps demonstrate compliance with various data regulations by providing clear, auditable trails of data movement and transformation.
- Facilitation of Data Discovery and Accessibility: Data lineage tools often include metadata management features, which make it easier for users to discover and access the data they need.
- Optimization of Data Processing: By understanding the flow of data, organizations can identify redundant processes and bottlenecks, leading to more efficient data processing workflows.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: A clear understanding of data flows and transformations fosters better collaboration among data teams, IT departments, and business stakeholders, leading to more cohesive and informed decision-making processes.
Common Data Lineage Challenges and Solutions
Even with the best tools and practices, organizations face obstacles when implementing data lineage. Here are the most common challenges and how to overcome them:
Challenge 1: Incomplete Coverage
The Problem: Your lineage tool can't capture everything in your complex data environment. Legacy systems, manual processes, and spreadsheet-based workflows create gaps.
The Solution:
- Accept that 100% automated lineage isn't realistic for most organizations
- Supplement automated capture with manual documentation for key gaps
- Prioritize coverage based on business criticality, not completeness
- Create "lineage markers" for manual processes that document inputs and outputs, even if you can't track internal logic
- Accept that 100% coverage isn't necessary, focus on business-critical paths
Challenge 2: Manual Lineage Maintenance
The Problem: Without automation, lineage documentation becomes outdated as code and systems evolve. Teams spend significant time manually updating lineage diagrams that quickly become incorrect.
The Solution:
- Invest in automated lineage capture tools from the start
- Integrate lineage extraction into your CI/CD pipeline
- Avoid manual documentation except for unavoidable legacy systems
- Set up alerts when lineage hasn't been refreshed in a defined period
Challenge 3: Determining Appropriate Granularity
The Problem: Too granular (every single column transformation) creates overwhelming complexity. Too coarse (just system-to-system) lacks the detail needed for debugging.
The Solution:
- Offer multiple views: high-level for business users, detailed for technical users
- Provide filtering and search to help users focus on relevant portions
- Capture at column-level but allow users to collapse to table-level views
- Document critical transformations but summarize routine cleansing steps
Challenge 4: Getting Stakeholder Buy-In
The Problem: Data lineage requires investment in tools and time. Business stakeholders may not immediately see value, especially if they haven't experienced major data incidents.
The Solution:
- Start with a pilot focused on a known pain point (compliance reporting, frequent troubleshooting)
- Quantify time savings from faster debugging and impact analysis
- Demonstrate compliance benefits with concrete examples
- Share success stories from similar organizations
- Calculate ROI, including prevented incidents and faster migrations
Challenge 5: Resource and Expertise Requirements
The Problem: Implementing comprehensive lineage requires skills in data engineering, tool configuration, and metadata management. Smaller teams may lack these resources.
The Solution:
- Start with SaaS lineage tools that minimize configuration needs
- Leverage vendor professional services for initial setup
- Focus on automated capture to minimize ongoing maintenance
- Build lineage capabilities gradually as team expertise grows
- Prioritize quick wins that demonstrate value with minimal investment
FAQs
What is data lineage in simple terms?
Data lineage is a visual map showing where your data comes from, how it changes as it moves through your systems, and where it ends up. Think of it like tracking a package through the mail system. Lineage shows every stop the data makes, what happens to it at each stop, and who handles it along the way.
Why is data lineage important?
Data lineage is critical because it helps you trust your data, fix problems faster, and comply with regulations. When a report shows unexpected numbers, lineage lets you trace back to find the error in minutes instead of days. When regulators ask how you handle customer data, lineage provides documented proof. It turns data from a black box into a transparent, trustworthy asset.
What's the difference between data lineage and data provenance?
Data provenance answers "where did this data originally come from?" It focuses on the source or origin. Data lineage answers "what is the complete journey of this data?" It tracks the entire flow from source through all transformations to the final destination. Provenance is the starting point; lineage is the full story.
What's the difference between business and technical data lineage?
Business lineage focuses on how data supports business processes and decisions, which departments use what data, how revenue is calculated, and what reports executives rely on. Technical lineage focuses on the technical details, which tables feed which ETL jobs, what SQL transformations are applied, and how data moves between systems. Business users need business lineage; data engineers need technical lineage.
What are the main benefits of data lineage?
The top benefits are: (1) Faster troubleshooting when data issues occur 70% time reduction on average, (2) Impact analysis before making changes see what will break before you break it, (3) Regulatory compliance automated audit trails for GDPR, HIPAA, etc., (4) Improved data trust transparency builds confidence in data quality, (5) Efficient migrations understand dependencies and prioritize what to migrate.
What techniques are used to capture data lineage?
Four main techniques: (1) Parsing - automatically analyzing ETL code and SQL to extract lineage, (2) Tagging - attaching metadata to data as it moves, (3) Pattern-based - identifying common transformation patterns and applying them, (4) Self-contained - embedding lineage metadata within datasets themselves. Most modern tools use parsing for automation.
What tools are commonly used for data lineage?
Popular tools include enterprise platforms (OvalEdge, Collibra, Alation, Informatica), modern data stack tools (Monte Carlo, Atlan, Datafold), and open source options (Apache Atlas, OpenLineage, Marquez). The best tool depends on your data environment, budget, and whether you prioritize governance, observability, or catalog capabilities.
How long does it take to implement data lineage?
For a pilot focused on critical pipelines: 2-4 weeks. For automated lineage across your core data warehouse: 2-3 months. For enterprise-wide comprehensive lineage: 6-12 months. Start small with high-impact use cases to demonstrate value quickly, then expand coverage over time.
What industries benefit most from data lineage?
Any industry handling sensitive data or facing regulatory requirements benefits significantly. Financial services (regulatory reporting, audit trails), healthcare (HIPAA compliance, patient data tracking), retail and e-commerce (personalization pipelines, revenue reporting), telecommunications (customer analytics, network data), and manufacturing (supply chain visibility) all see major value from data lineage.
How does data lineage help with compliance?
Data lineage creates automatic audit trails showing exactly how you collect, store, transform, and delete data. When regulators ask, "how do you handle personal data?" you can provide visual diagrams showing the complete journey. For GDPR data deletion requests, lineage maps every location where individual data exists. For HIPAA, lineage proves data security controls at every step. This documentation passes audits faster and reduces compliance risk.
Getting Started with Data Lineage
Data lineage has evolved from a nice-to-have documentation practice to an essential capability for modern data organizations. As data environments grow more complex and regulatory requirements become more stringent, lineage provides the transparency and control needed to maintain data quality and trust.
Whether you're debugging a production issue, planning a cloud migration, responding to compliance audits, or simply trying to understand where a number in a report comes from, data lineage transforms guesswork into confidence.
Ready to implement data lineage in your organization?
📥 Download our Data Lineage Implementation Guide
🎯 See how OvalEdge automates data lineage capture
📚 Explore more data governance best practices
🎓 Learn about data governance frameworks
💡 Discover data governance use cases
About OvalEdge
OvalEdge provides modern data governance and catalog solutions that help organizations discover, understand, and trust their data. Our automated data lineage capabilities capture relationships across your entire data ecosystem, providing the transparency you need for confident decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Schedule a Demo | Explore OvalEdge Academy
Book a call with us to find out:
|
Deep-dive whitepapers on modern data governance and agentic analytics

OvalEdge Recognized as a Leader in Data Governance Solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.


