Table of Contents
Understanding BCBS 239: Key Principles & Risk Data Aggregation
BCBS 239 is a regulatory framework designed to improve risk data aggregation and reporting in banks, ensuring accurate, timely, and comprehensive data for decision-making. It applies to large, systemically important banks but is relevant to smaller institutions as well. OvalEdge supports compliance by streamlining data governance, automating reporting, and ensuring audit-ready, high-quality risk data for regulatory adherence.
Banks still face challenges with fragmented risk data scattered across departments and systems. This lack of cohesion is evident, as only 2 out of 31 Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs) are fully compliant with BCBS 239, underscoring the widespread gap in data aggregation and risk management practices.
This fragmentation leaves decision-makers blind when market turbulence strikes, leading to delayed reactions, miscalculated exposures, and compliance failures.
BCBS 239 changes that by enforcing rigorous standards for how banks aggregate, validate, and report their risk data. It provides a clear, globally accepted framework that transforms disjointed risk snapshots into a unified, reliable view that can alert senior leadership in minutes when systemic risk mounts.
If your institution is preparing to meet BCBS 239 compliance requirements, this guide will cut through the complexity. We’ll walk you through the 14 core principles, unpack what they mean in real‑world banking operations, surface the common implementation hurdles, and show you how data governance tools like OvalEdge can help you build a compliant, audit-ready RDARR infrastructure that lasts.
What is BCBS 239, and why does it matter?
BCBS 239 is a set of regulatory guidelines established by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision to enhance risk management and data governance in financial institutions. It focuses on improving liquidity risk measurement, stress testing, and ensuring transparency in capital reporting.
The framework aims to strengthen the resilience of banks by ensuring accurate risk data aggregation and aligning internal controls with global banking regulations.
Compliance with BCBS 239 is essential for mitigating systemic risk and fostering long-term financial stability. Institutions must implement robust systems for managing risks and reporting capital adequacy under these standards.
Origin: Why BCBS 239 was introduced
The 2008 financial crisis exposed severe weaknesses in banks' risk management practices. Financial institutions were unable to effectively measure or manage systemic risk, which contributed to widespread economic disruption.
According to Deloitte’s BCBS 239 Benchmark Survey, 69% of banks are planning to implement end-to-end data lineage, which remains a major hurdle for full compliance.
The Basel Committee recognized that to safeguard global financial stability, a new standard for risk data aggregation and reporting was required. BCBS 239 was introduced to ensure that banks could gather accurate, timely, and complete risk data from all departments and systems, making it accessible for decision-makers at all levels.
The ultimate goal was to create a system that would allow banks to identify potential risks quickly, adapt to market shocks, and comply with the evolving regulatory environment.
Who needs to comply: G‑SIBs, D‑SIBs, and beyond
BCBS 239 applies primarily to Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs) and Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs). G-SIBs are banks whose failure could trigger a global financial crisis due to their size, interconnectedness, and the role they play in the global economy. D-SIBs, while smaller, are still considered critical to the financial stability of their respective domestic markets.
The principles of BCBS 239 require these banks to adopt centralized risk data aggregation systems, ensuring that they can monitor and manage risks across all business units in real-time. Compliance includes establishing clear data governance frameworks, automating risk data aggregation, and ensuring timely reporting.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, BCBS 239 is becoming more relevant for a wider range of financial institutions. Smaller banks, regional players, and even fintech firms are starting to feel the pressure to adopt similar data aggregation practices to stay competitive and meet regulatory expectations.
Core objectives: Risk data aggregation & risk reporting (RDARR)
The core of BCBS 239 lies in risk data aggregation and reporting (RDARR). The aim is to ensure that banks can aggregate their risk data from all sources in a consistent, accurate, and timely manner, which is critical for effective decision-making during times of financial crisis.
-
Risk data aggregation ensures that all data, whether it’s related to liquidity, credit risk, or operational risk, is collected from various parts of the organization and made available in a central system.
-
Risk reporting focuses on how this aggregated data is shared with key stakeholders. BCBS 239 emphasizes that risk reports must be clear, accurate, and actionable, ensuring that senior management and regulators can make informed decisions quickly.
Together, these objectives form the RDARR framework, which is essential not only for regulatory compliance but for ensuring that financial institutions can manage and mitigate risk in a way that enhances overall financial stability. BCBS 239 pushes institutions to move away from disconnected, siloed risk data to a more integrated, transparent, and proactive approach to risk management.
|
Stat: Forrester's research cited by IBM highlights that over 25% of global data and analytics staff estimate their organizations lose over USD 5 million annually due to poor data quality, underscoring the importance of robust data management frameworks like BCBS 239. |
The 14 principles of BCBS 239 (at a glance)
BCBS 239 lays out 14 guiding principles for effective risk data aggregation and reporting (RDARR). These principles are divided into two core categories: governance and risk data aggregation practices.
-
Governance focuses on setting up strong data stewardship frameworks to ensure compliance. These principles emphasize the need for clear data ownership, proper infrastructure, and accountability.
-
Risk Data Aggregation addresses how banks should collect, aggregate, and report risk data in a manner that is accurate, timely, and complete.
The principles guide how banks should manage risk data across various levels of the organization and ensure data is easily accessible for decision-makers.
With clear guidance on both the structural and technical aspects, BCBS 239 ensures that banks have the appropriate frameworks and tools to manage risk data effectively, which is crucial for making informed decisions in times of financial uncertainty.
Summary table of all 14 principles
Below is a concise table summarizing the 14 principles of BCBS 239, offering a quick reference to understand each principle at a glance:
|
Principle |
Description |
|
Principle 1: Governance |
Establish a strong governance framework to oversee data aggregation and reporting processes. |
|
Principle 2: Data Architecture & IT Infrastructure |
Ensure scalable and flexible IT systems to support risk data aggregation. |
|
Principle 3: Accuracy |
Implement systems that ensure data integrity, validation, and accuracy in aggregation. |
|
Principle 4: Completeness |
Aggregate all critical risk data across business lines to provide a comprehensive view of exposure. |
|
Principle 5: Timeliness |
Aggregate and report risk data in real-time or near-real-time to allow for timely decision-making. |
|
Principle 6: Adaptability |
Design systems that can adapt to new regulatory requirements and evolving business conditions. |
|
Principle 7: Report Accuracy |
Ensure that risk reports are accurate and reflect true risk exposure. |
|
Principle 8: Report Comprehensiveness |
Design reports that cover all critical risk areas to provide a holistic view. |
|
Principle 9: Clarity & Usefulness |
Ensure that risk reports are clear and actionable for decision-makers. |
|
Principle 10: Report Frequency |
Establish appropriate reporting frequency based on the urgency and significance of risk data. |
|
Principle 11: Report Distribution |
Distribute reports efficiently to stakeholders at all levels of the organization. |
|
Principle 12: Supervisory Review |
Implement effective supervisory reviews to ensure that BCBS 239 compliance is being met. |
|
Principle 13: Remedial Actions & Supervisory Measures |
Take corrective actions if non-compliance is found, and develop supervisory measures to address gaps. |
|
Principle 14: Supervisory Cooperation |
Foster collaboration between home and host supervisors for effective global oversight. |
These principles not only guide data aggregation and reporting practices but also ensure that the organizational structures needed for effective risk management are in place. By adhering to these principles, financial institutions can ensure they are on track to meet the rigorous standards of BCBS 239.
Deep dive: What each principle means in practice
BCBS 239 is designed to ensure that financial institutions can manage and report risk data in a structured, transparent, and consistent manner. While the principles themselves provide a solid framework, the real challenge lies in putting them into practice.
Let’s break down each principle and see how it applies to the day-to-day operations of a bank, highlighting both the technical and organizational steps required to meet these standards.

Governance & infrastructure
The foundation of BCBS 239 compliance starts with strong governance and robust infrastructure. Let’s explore what each of these principles requires:
- Principle 1: Governance
Effective governance frameworks are essential for managing risk data across the organization. Principle 1 mandates that banks establish a centralized governance structure to oversee all risk data aggregation and reporting activities.
This ensures that data management practices are standardized across departments, reducing the risk of errors and discrepancies in the data. Clear data ownership and accountability are necessary for effective oversight.
In practice: A bank should appoint a dedicated risk data governance team responsible for setting data standards, managing data quality, and ensuring compliance across the organization. This team must work with business units to ensure that risk data is accurate, reliable, and reported consistently.
-
Principle 2: IT infrastructure
Principle 2 stresses the importance of having scalable, flexible IT systems in place. As the volume of risk data continues to grow, financial institutions must have infrastructure that can handle large datasets, accommodate rapid changes, and support the evolving regulatory environment.
In practice: A bank’s IT infrastructure needs to be capable of processing vast amounts of data in real time. This requires investment in modern data storage solutions, cloud-based technologies, and automated data aggregation tools. It also requires the integration of legacy systems with new technology, ensuring they work seamlessly together.
Risk data aggregation capabilities
Data aggregation is at the heart of BCBS 239. This section outlines the principles that ensure the data is accurate, complete, and timely, which is critical for effective risk management.
-
Principle 3: Accuracy
Accuracy in risk data aggregation is essential to provide a true reflection of an institution’s risk profile. Principle 3 mandates that institutions must validate and verify data at all stages of aggregation to ensure its integrity.
In practice: Financial institutions need to implement robust data validation procedures, including checks for data consistency, data completeness, and correct categorization. This involves setting up automated validation rules that flag discrepancies early in the process, preventing errors before they can affect reporting.
-
Principle 4: Completeness
Principle 4 ensures that all critical risk data is captured. Incomplete data can lead to missed risks or misinformed decisions, which can undermine the stability of the institution.
In practice: Institutions must establish comprehensive data collection processes that span all risk areas, such as credit, market, operational, liquidity, and more. Each department within the bank should be required to contribute to a central risk data repository to ensure that no relevant data is left out.
-
Principle 5: Timeliness
Timeliness is crucial during periods of financial crisis. Principle 5 requires that risk data be aggregated in real time or near real-time to enable swift decision-making when needed.
In practice: Banks need to automate data aggregation to ensure that risk reports are generated instantly and are available for decision-makers in real time. This may involve setting up automated dashboards and real-time reporting tools that provide stakeholders with up-to-the-minute risk data.
-
Principle 6: Adaptability
The financial industry is constantly evolving, and Principle 6 emphasizes the need for systems that can quickly adapt to new regulatory requirements and emerging risks.
In practice: Banks must ensure that their data aggregation systems are modular and flexible. This includes regularly updating systems to incorporate new regulations, integrating emerging data sources, and using advanced analytics to identify new or hidden risks as they arise.
Risk reporting practices
Effective risk reporting is one of the most vital components of BCBS 239. This section focuses on how to present the aggregated risk data to key stakeholders in a way that’s accurate, clear, and actionable.
-
Principle 7: Report accuracy
Ensuring the accuracy of risk reports is essential for effective decision-making. Principle 7 requires that risk data reported to senior management, regulators, and other stakeholders is truthful and without bias.
In practice: Banks need to implement review processes for all risk reports to confirm that the data presented is accurate. This may involve cross-checking reports against primary data sources and applying consistent metrics to risk categories.
-
Principle 8: Report comprehensiveness
Principle 8 stresses the importance of reporting all critical risk areas, ensuring that no major risks are overlooked.
In practice: Financial institutions should create comprehensive risk reports that cover all aspects of risk exposure. This includes not only financial risk but also operational, strategic, and reputational risks. The reports should provide a 360-degree view of the bank's risk landscape.
-
Principle 9: Clarity & usefulness
Principle 9 ensures that risk reports are clear and actionable, tailored to meet the needs of different stakeholders, whether they’re board members, managers, or regulators.
In practice: Banks must design their risk reports with the audience in mind, making them easy to understand and relevant to the decision-making process. This could involve creating visual reports, like dashboards or graphs, that make it easier to digest complex data.
-
Principle 10: Report frequency
The frequency of risk reporting is crucial for timely decision-making. Principle 10 recommends that reports be generated at appropriate intervals, based on the urgency of the data.
In practice: Risk reports should be delivered on a regular schedule (e.g., daily, weekly) for routine risk monitoring, while additional ad-hoc reports may be needed in response to sudden market changes or crises.
-
Principle 11: Report distribution
Once a report is ready, it must be distributed efficiently to stakeholders. Principle 11 emphasizes that the right people must receive the right data at the right time.
In practice: Banks should set up automated distribution systems that push reports to designated stakeholders. Reports should be easily accessible to both internal and external stakeholders, including regulatory bodies.
Supervisory review & cooperation
Finally, BCBS 239 outlines supervisory processes to ensure compliance with these principles and maintain consistency across the global financial system.
-
Principle 12: Supervisory review
Effective supervisory review is critical to ensuring that BCBS 239 compliance is maintained. Principle 12 requires that regulators regularly assess banks’ adherence to the framework and intervene when necessary.
In practice: Banks must establish ongoing review processes to ensure that their risk data aggregation and reporting practices meet regulatory expectations. Regular audits and assessments should be conducted to identify areas for improvement.
-
Principle 13: Remedial actions & supervisory measures
If banks fail to comply with BCBS 239, regulators must take corrective action. Principle 13 outlines the need for timely and effective remedial measures to address compliance gaps.
In practice: When a bank is found non-compliant, regulators may impose fines or require changes to data management systems. Institutions should develop a response plan that includes clear actions for addressing compliance failures.
-
Principle 14: Supervisory cooperation
As financial institutions operate in multiple jurisdictions, global cooperation among regulators is essential for ensuring consistent oversight. Principle 14 emphasizes the importance of home-host supervisory cooperation.
In practice: Financial institutions with global operations must ensure that they work closely with regulators in different jurisdictions to align their risk data aggregation practices and meet local requirements.
|
Did you know? 72% of banks have defined a data quality risk appetite, but only 17% have operationalized it, highlighting the need for robust governance tools. |
Why BCBS 239 compliance still matters in 2026
As we move towards 2026, the need for BCBS 239 compliance has only grown more important. The financial landscape is evolving rapidly, with new regulatory challenges and increased global financial risks.
For banks, adapting to these changes and ensuring compliance with BCBS 239 is crucial for managing risks effectively and maintaining operational stability.
Let’s explore why BCBS 239 remains essential for the future of banking.
1. Regulatory pressure & evolving expectations
As global financial risks rise, regulators are tightening their expectations. BCBS 239 serves as a cornerstone for managing systemic risk, but compliance requirements are becoming more stringent. Financial institutions must adapt to meet these evolving standards.
-
Real-time risk visibility is now expected.
-
Robust reporting frameworks are essential.
-
Institutions must update data management practices regularly to stay compliant and competitive.
Adapting to these evolving regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure long-term success in an increasingly regulated environment.
2. Operational resilience & risk governance
In 2026, operational resilience is a top priority for banks. BCBS 239 helps institutions strengthen their ability to respond to financial shocks by centralizing risk data aggregation.
-
Data accuracy is critical for decision-making.
-
Centralized governance frameworks ensure comprehensive risk management.
-
Banks can proactively mitigate risks with real-time, reliable data.
This centralized approach ensures that banks can maintain continuity and respond effectively to disruptions.
3. Support for advanced analytics, AI & data-driven risk management
BCBS 239 enables financial institutions to leverage AI and advanced analytics by ensuring high-quality, well-organized data. With the framework’s focus on data governance, banks can use AI tools to predict risks and make data-driven decisions.
-
AI and analytics help identify risks faster.
-
Data governance ensures reliable, traceable data for AI models.
-
Proactive decision-making becomes easier with predictive insights.
By embracing BCBS 239, institutions can better manage financial risks and stay ahead of potential threats.
|
Also read: Data Governance Risk Management Guide 2026 |
Common challenges & pitfalls in implementation
Implementing BCBS 239 can be a complex process. Despite its importance, many institutions face hurdles that can hinder compliance. Legacy systems, manual processes, and unclear data ownership create inefficiencies that must be addressed. Let’s explore the main challenges banks encounter and how to overcome them.
-
Legacy systems & data silos: Outdated legacy systems limit effective data aggregation, creating data silos. This makes it hard to get a unified view of risk. Modernizing systems and integrating data across departments is crucial for compliance.
-
Manual processes & spreadsheet-based reporting: Relying on manual processes and spreadsheets increases the risk of errors and inefficiencies. Automating data aggregation and reporting processes streamlines operations, ensuring more accurate and timely reports.
-
Lack of clear data ownership: Clear data ownership is essential for BCBS 239 compliance. Without it, accountability is lost, and managing data quality becomes challenging. Assigning clear roles for data stewardship ensures responsible data management.
-
Insufficient data lineage, quality controls, & auditability: Without proper data lineage and quality controls, auditability is compromised. This makes compliance difficult. Implementing strong data governance practices, including data validation, ensures that risk data is traceable and reliable.
-
Complexity across legal entities: Implementing BCBS 239 across multiple legal entities and jurisdictions can be complex due to varying regulatory requirements. Standardizing data management practices and collaborating with local regulators simplifies this process.
By addressing these common challenges, banks can set themselves up for successful BCBS 239 compliance, improving their overall risk management practices.
A practical BCBS 239 implementation guide
Implementing BCBS 239 requires a well-structured, step-by-step approach. Below is a guide that outlines the key stages of the implementation process, helping banks navigate the complexities of compliance and build a robust risk data aggregation and reporting system.
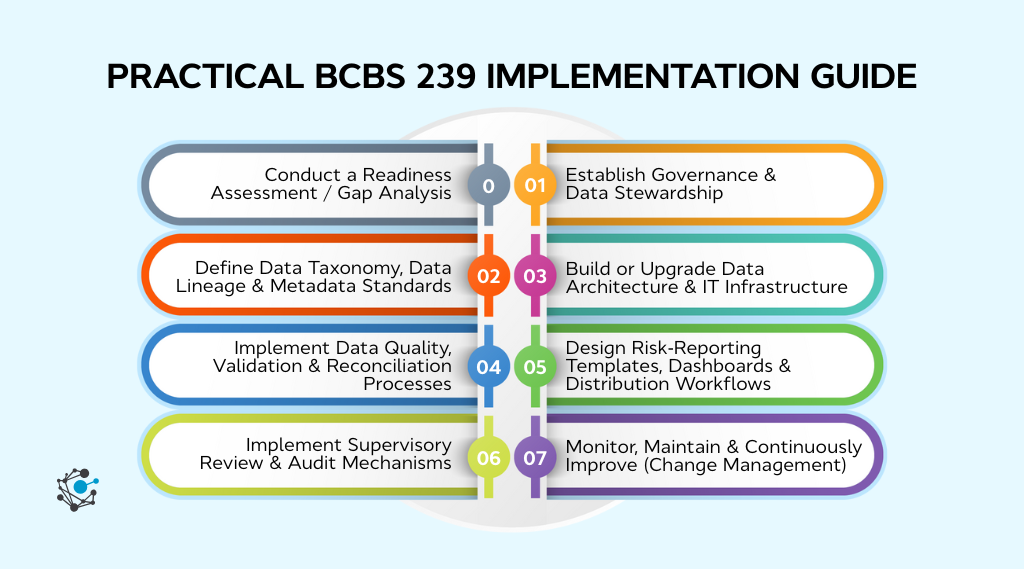
Step 0: Conduct a readiness assessment/gap analysis
Start by assessing your current systems for data aggregation and reporting. Identify gaps in your processes, data quality, and reporting capabilities. This gap analysis will provide a baseline for your BCBS 239 compliance journey. Tools like data audits and maturity assessments can help pinpoint areas that need improvement.
Step 1: Establish governance & data stewardship
Set up a strong data governance framework, including appointing data owners and stewards. Assign clear roles and responsibilities to ensure data is managed, validated, and reported accurately. Effective governance is key to maintaining data consistency and reliability across the organization.
Step 2: Define data taxonomy, data lineage & metadata standards
Establish a standardized data taxonomy to organize risk data. Implement a data lineage framework to trace data origins and transformations. Set metadata standards to ensure consistent and understandable data integration across systems.
Step 3: Build or upgrade data architecture & IT infrastructure
Evaluate your current IT infrastructure to identify areas that need upgrading. Ensure your systems can handle large volumes of risk data, support real-time aggregation, and integrate with other data sources. Scalable and flexible infrastructure is vital for long-term BCBS 239 compliance.
Step 4: Implement data quality, validation, & reconciliation processes
Set up robust data validation and reconciliation processes to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Regularly validate data to catch discrepancies early and ensure reliable reports.
Step 5: Design risk-reporting templates, dashboards & distribution workflows
Develop risk-reporting templates that align with BCBS 239’s requirements. Create automated workflows for efficient report generation and distribution to stakeholders, ensuring timely access to key risk data.
Step 6: Implement supervisory review & audit mechanisms
Build a review process to ensure compliance with BCBS 239. Implement audit mechanisms to track adherence and identify areas for improvement, ensuring continuous monitoring and accountability.
Step 7: Monitor, maintain, & continuously improve
Set up ongoing monitoring systems to track compliance progress. Regularly update processes, address gaps, and refine reporting practices. Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining long-term BCBS 239 compliance.
By following these steps, banks can implement BCBS 239 effectively, ensuring compliance while building a resilient, data-driven risk management framework that supports long-term financial stability.
|
Fun fact: Poor data quality costs organizations at least USD 13 million annually on average, according to Gartner. |
How modern data governance & tools help compliance
Achieving BCBS 239 compliance is a complex process that requires the right tools and frameworks to ensure data is accurate, traceable, and accessible. Modern data governance platforms, like OvalEdge, help institutions streamline data management processes, enabling them to meet the stringent requirements of BCBS 239.
These tools play a vital role in improving data discoverability, enhancing reporting accuracy, and ensuring timely compliance.
1. The role of data catalogs, metadata management, & data lineage platforms
Data catalogs, metadata management tools, and data lineage platforms are essential for managing the vast amounts of risk data required by BCBS 239. These tools enable financial institutions to:
-
Improve data discoverability: Data catalogs provide a centralized repository where all risk data can be easily located and accessed by stakeholders.
-
Enhance data traceability: Metadata management ensures that data can be traced across systems, which is crucial for verifying data integrity and ensuring it aligns with BCBS 239 standards.
-
Enable transparency: By maintaining a clear view of where data comes from and how it moves through systems, institutions can enhance accountability and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Platforms like OvalEdge make it easier to manage these elements, providing a clear and actionable overview of all data and its lineage, thus making the process of BCBS 239 compliance smoother and more effective.
2. Automating data quality, validation & reconciliation
Automation is a game-changer when it comes to improving data quality and validation. Manual processes are not only time-consuming but also prone to errors, which can lead to inaccurate risk reporting and potential compliance issues. By automating key processes, institutions can:
-
Enhance data quality: Automation ensures that risk data is consistently validated against predefined rules, reducing the risk of errors.
-
Accelerate validation & reconciliation: Automation streamlines the process of validating and reconciling data, ensuring that reports are generated faster and with higher accuracy.
Using automated tools to validate and clean data minimizes manual intervention and ensures that risk data is ready for analysis and reporting. OvalEdge helps automate these processes, making it easier to maintain high-quality, compliant data.
3. Building audit-ready risk reporting pipelines
One of the key challenges of BCBS 239 compliance is ensuring that risk data reporting is both accurate and ready for regulatory review. Building audit-ready reporting pipelines is critical for:
-
Ensuring timeliness: Automated reporting pipelines ensure that risk data is available on time and can be distributed to relevant stakeholders promptly.
-
Maintaining consistency: By standardizing the reporting process, banks can ensure that risk reports are consistent and meet regulatory requirements each time.
-
Enabling compliance: These pipelines should be designed with auditability in mind, ensuring that reports are easily traceable for regulatory scrutiny.
OvalEdge helps financial institutions set up these audit-ready pipelines by providing a unified platform for data integration, validation, and reporting. With the right governance tools, institutions can confidently meet BCBS 239 reporting requirements while minimizing manual effort.
Checklist for BCBS 239 compliance
To help guide your BCBS 239 compliance journey, here’s a simple yes/no checklist outlining the key steps to follow. This checklist ensures that you're covering all essential aspects of compliance, from governance to risk reporting.
|
By completing this checklist, you can ensure that your institution is on the right path to meeting BCBS 239 compliance requirements. Regularly review and update these steps to maintain long-term compliance and strengthen your risk management processes.
Modern data governance tools like OvalEdge are invaluable in helping financial institutions comply with BCBS 239. They improve data traceability, enhance data quality, and automate risk reporting processes, all of which are essential for ensuring that data is ready for regulatory review and is in line with BCBS 239's stringent standards.
If you're ready to take your BCBS 239 compliance to the next level, book a demo with OvalEdge today and see how we can help streamline your compliance process.
Conclusion
BCBS 239 has become the gold standard for risk data aggregation and reporting, offering financial institutions a framework for managing risks more effectively. By adopting the principles of BCBS 239, banks can improve risk management, make better decisions, and remain agile as they navigate evolving regulations.
But compliance isn’t always easy. Outdated systems, fragmented data, and manual processes can make the journey challenging. This is where OvalEdge comes in.
Our data governance platform helps streamline the implementation of BCBS 239 by automating data aggregation, ensuring data quality, and creating audit-ready reporting pipelines. With OvalEdge, you can simplify compliance, improve decision-making, and stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
If you want to explore how OvalEdge can make BCBS 239 compliance easier and more effective, schedule a free demo today.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of BCBS 239?
BCBS 239 aims to improve risk data aggregation and reporting in banks, ensuring accurate, timely, and comprehensive data to support effective decision-making, especially during financial crises.
2. How does BCBS 239 impact smaller banks?
Although originally designed for large institutions, BCBS 239’s principles are increasingly relevant for smaller banks, as regulatory bodies expand compliance expectations for financial stability and data transparency across the sector.
3. Why is automation critical for BCBS 239 compliance?
Automation reduces manual errors, speeds up data aggregation, and ensures timely risk reporting, which is crucial for meeting BCBS 239’s requirements and staying compliant in a fast-changing regulatory landscape.
4. What role does data governance play in BCBS 239 compliance?
Data governance ensures that risk data is accurate, complete, and accessible across the institution, providing a framework to manage data quality, ownership, and accountability, key aspects of BCBS 239 compliance.
5. How can OvalEdge help with BCBS 239 implementation?
OvalEdge simplifies BCBS 239 compliance by providing tools for data governance, automation of risk reporting, and creating audit-ready pipelines, ensuring timely and accurate data aggregation for regulatory requirements.
6. What challenges do banks face with BCBS 239 compliance?
Banks struggle with legacy systems, data silos, manual processes, and unclear data ownership, which complicate compliance with BCBS 239’s standards for accurate and timely risk data aggregation and reporting.
OvalEdge recognized as a leader in data governance solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.


.png)
.webp)


