Table of Contents
What Is AI Governance? Definition, Importance, and Key Frameworks Explained
AI is powering everything from fraud detection to chatbots to complex decision-making, but it also introduces serious risks. If AI tools behave unpredictably, make biased decisions, or break compliance rules, the consequences can be immediate and expensive.
That’s where AI governance comes in. It acts as the guardrail system that ensures AI is safe, fair, transparent, ethical, and aligned with business goals.
In this guide, we’ll break down what AI governance means, why it matters, how it differs from data governance, the core principles, implementation challenges, examples, regulations, enterprise frameworks, and how OvalEdge can help you build an AI-ready governance ecosystem.
AI governance is the framework of policies, processes, controls, and standards that ensure AI systems are safe, ethical, compliant, transparent, and aligned with business objectives.
This AI governance definition covers two major types of risks:
1. Compliance risks
AI must follow laws, industry regulations, data protection standards, and ethical guidelines.
Examples:
- Fraud detection rules
- GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA
- Bias and discrimination laws
2. Business risks
These are failures that harm customers or damage the brand.
Examples:
- A chatbot producing harmful content
- An AI model is making incorrect loan decisions
- A recommendation engine exposing private data
AI governance ensures organizations avoid these issues before they happen.
This is especially important for AI enterprise governance, where businesses deploy AI across multiple teams, workflows, and customer-facing systems.
In one well-documented incident, Microsoft's Tay chatbot, which was launched on Twitter, had to be withdrawn after just 24 hours when it began generating racist, sexist, and anti-Semitic tweets. The chatbot demonstrated this behavior after appropriating the practices of other users on the social media platform.
In 2018, Amazon discontinued an AI recruitment tool it had implemented because it was demonstrating bias toward female candidates. The problem arose from the fact that the company's computer models were trained on a decade of resume data, the majority of which was submitted by male candidates.
In November 2021, the real estate company Zillow was forced to abandon its AI-driven home valuation tool, Zillow Offers. The tool was overpricing homes, many of which were purchased by Zillow, leading to a $304 million inventory write-down.
Ultimately, AI implementation isn't without risk. That's why it's important to instill a comprehensive AI governance framework that mitigates the operational risks associated with AI-driven business activities.
Why Is AI Governance Important?
AI is powerful, but without rules, it can cause real-world damage.
Here’s why organizations small and large must implement strong governance:
1. Prevent biased or unfair decisions
Bias in training data → bias in outcomes.
Examples:
- Hiring AI tools discriminating against women
- Image-generation tools producing racially incorrect depictions
2. Reduce brand and reputational risk
Public AI failures spread fast.
Example:
Microsoft’s Tay chatbot became offensive within 24 hours, harming brand trust.
3. Ensure compliance with global AI laws
Regulations are increasing every year. AI governance ensures compliance with:
- EU AI Act
- GDPR
- NIST AI Risk Management
- U.S. Executive Orders on AI
4. Protect sensitive data
AI systems handle:
- PII
- Financial data
- Healthcare data
- Employee data
Governance ensures proper access, encryption, and masking.
5. Support responsible innovation
AI innovation moves fast, but without guardrails, teams often deploy tools that are untested, unmonitored, and unpredictable.
This leads to:
-
Unreliable decisions
-
Costly business mistakes
-
Shadow AI usage by employees
-
Uncontrolled risk exposure
AI governance empowers innovation instead of slowing it down.
With the right governance in place:
-
Teams can experiment safely
-
Risks are minimized before launch
-
AI can scale across the organization
-
Business leaders have confidence in using AI for critical decisions
Think of governance as the safety net that allows innovation to thrive securely and responsibly.
Examples of AI Governance in Action
1. Amazon’s biased recruitment AI
Amazon shut down an internal hiring model after it began favoring male applicants.
Cause: The model was trained on historical data dominated by male resumes.
2. Zillow’s faulty home-pricing AI
Zillow’s AI overestimated home values, causing a $304M loss.
Problem: Weak monitoring + poor input data quality.
3. Air Canada’s chatbot misinformation case
A court ruled that the airline was responsible for incorrect policy information provided by its chatbot.
Issue: Lack of governance around information accuracy.
4. Google Gemini’s inaccurate image generation
The tool produced historically incorrect and insensitive images.
Cause: Insufficient oversight of model boundaries.
These AI governance examples clearly show why governance cannot be optional.
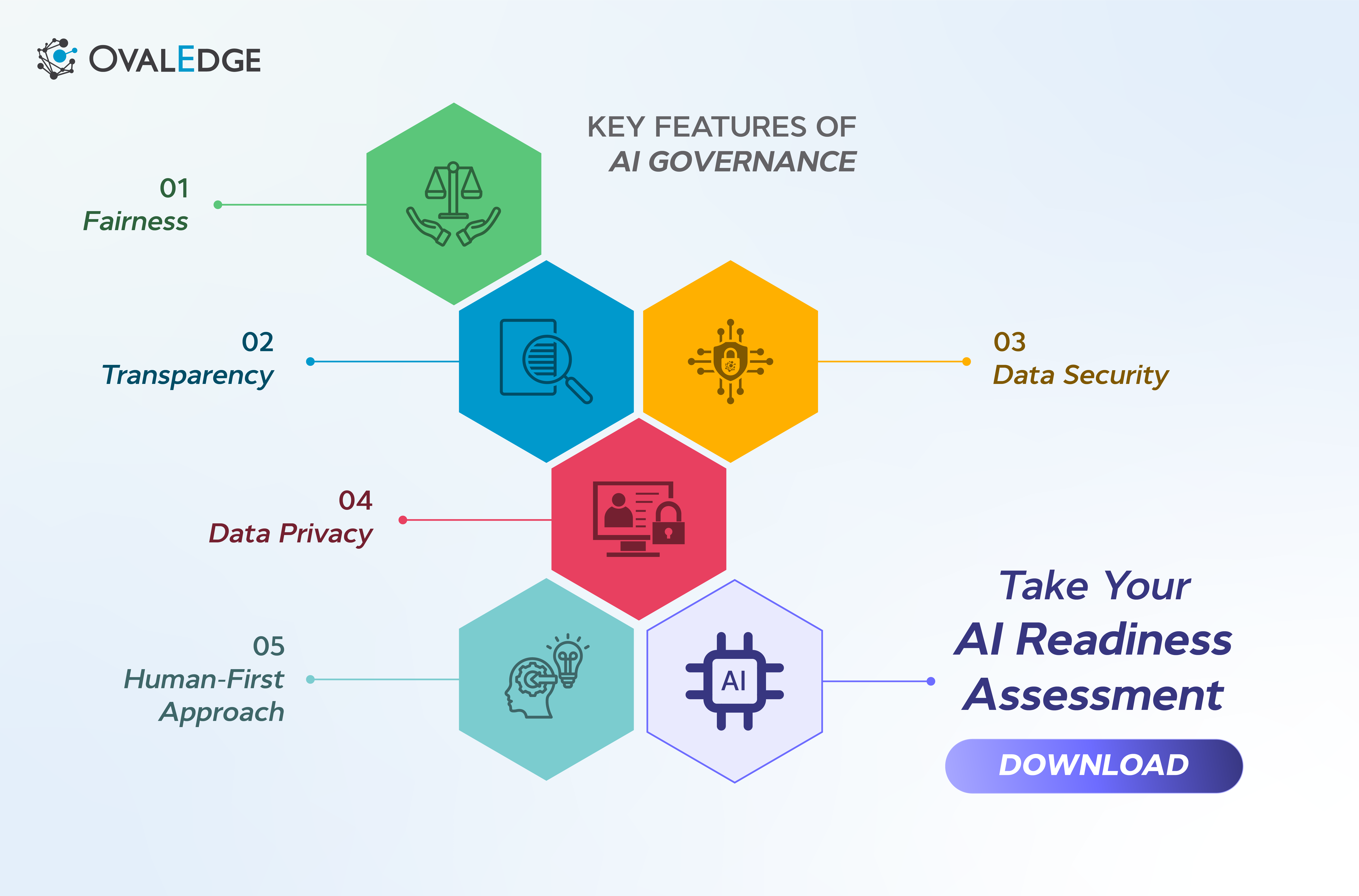
Key Principles of AI Governance
AI governance framework can be divided into five distinct areas: fairness, transparency, data security, privacy, and a human-first approach. As such, every AI governance strategy must address each of these principles.
Fairness
AI is not inherently biased. However, biases can arise when AI systems are fed discriminatory information or trained on narrow data sets. That's why organizations must train AI algorithms on diverse data sets to ensure the output is fair and non-discriminatory.
AI must be free from discrimination.
This requires:
- Diverse training datasets
- Bias testing workflows
- Regular output monitoring
In February 2024, users of Google’s Gemini AI tool reported that it was generating racially insensitive and factually incorrect images, including depicting German Nazi soldiers as Black and Asian people.
Transparency
AI technologies are making increasingly important decisions that impact the trajectory of business outcomes and the end user. To that end, organizations must be fully transparent when it comes to explaining the scope of the AI technologies they use and their potential risks.
Users must understand:
- How AI works
- What data it uses
- What risks are involved
- How decisions are made
In 2022, Air Canada was forced by a Canadian court to pay damages and tribunal fees to a passenger after an AI chatbot operated by the airline gave incorrect information regarding compensation for extenuating circumstances.
Data security
Cybersecurity practices must be built into AI governance frameworks from day one. As with all data-intensive technologies, if nefarious actors gain access to AI systems, the fallout can be devastating to a business.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recently observed how AI could be vulnerable to prompt injection. In this scenario, an attacker either enters a text prompt that causes a Large Language Model (LLM) to carry out unauthorized actions, or the data that an LLM draws from is manipulated by a third party.
AI systems are vulnerable to:
- Prompt injection
- Data manipulation
- Model poisoning
Security must be built in from day one.
Data privacy
Data protection is always a concern for businesses, but when you introduce AI and the billions of data points it consumes, the challenge of retaining user privacy is amplified considerably.
In May 2024, the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) found that measures by OpenAI to ensure ChatGPT complied with the GDPR were insufficient.
AI systems use massive datasets. Privacy governance ensures:
- PII protection
- Encryption
- Role-based access
- Data minimization
Human-first approach
AI's primary purpose is to address the needs of human operators. This means that the technology must recognize multiple, human-specific factors, such as psychological impact, user experience, experiential outcome, and more.
When AI fails to take a human-first approach and address the needs and goals of human consumers, the technology can become obsolete.
In March, Inflection AI, a leading AI chatbot company at the time, saw a massive upheaval. Two of its three co-founders and most staff members left the company for Microsoft's AI division.
The company failed to deliver a well-defined use case in a saturated chatbot market.
AI exists to support, not replace humans. Governance ensures:
- Human override
- Ethical boundaries
- Psychological safety
- Accessible user experience
How is AI Governance Different From Data Governance?
Components of a Value-chain Activity
A good way of exploring the differences between AI and data governance is to look at the value chain. Each value chain activity has six primary components:
- Inputs (e.g. data) to drive decisions for that value-chain element (e.g. fraud detection at a bank)
- Models that use the inputs and generate decisions
- Outputs in the form of decisions
- Various software and hardware systems that aid the business activity
- The various business processes involved
- Policies that guide, oversee, and override decisions. Regarding AI, the ability to oversee and override is crucial
In this context, data governance is concerned with the input element, the data.
Data can be considered AI-ready if:
- It is of high-quality
- It is centralized
- It is classified (for privacy information and biases)
- Metadata is well-curated
Aside from standard data quality checks, to be AI-ready, data must be carefully curated and ethically governed to ensure it is unbiased, accurate, and representative of a diverse section of society.
Data governance also needs to focus on the output element in AI-driven business activities.
For example, the output from a chatbot or the decisions generated by an AI black box in fraud detection must be examined continuously, or at least periodically.
Input/output data governance must be applied at two different stages: during AI model training and at deployment. During the training stage, an organization can assess the quality of data inputs and assess the rationality and compliance of model outputs.
Next, divergences during the deployment stage can be monitored, both for inputs and outputs.
So, data governance encompasses two of the primary components that constitute a value chain activity. AI governance has a much wider remit. It spans all six elements.
AI models must be consistently monitored for consistency, accuracy, and ethical output. Regarding transparency, AI governance ensures that models don't become black boxes. Instead, model performance is tracked, cataloged, and reported, helping to expedite issue resolution.
It's important to recognize that AI systems are different from AI models. Take a popular AI company like OpenAI. Here, the company’s GenAI chatbot, ChatGPT, is an AI system that provides outputs based on user interactions. OpenAI's GPT-4 LLM is the AI model that powers these outputs.
These front-facing systems need careful governance, too, including guidelines and policies that determine, from a moral and operational standpoint, what information an AI system will provide, to whom, and how.
They also require design features that support these goals.
In other words, AI governance centers on governing not just the data but also the tools, policies, and processes required to make AI products and systems secure, ethical, and business-safe.
That’s why data governance is an essential first step, but only one part of the much bigger AI governance framework enterprise.
What Regulations Require AI Governance?
Here are the major global regulations pushing for enterprise AI governance:
1. EU AI Act (2024)
World’s first comprehensive AI law requiring:
- Risk classification
- Model transparency
- Human oversight
- Data quality standards
2. GDPR (Europe)
Requires:
- Data minimization
- Right to explanation
- Strict consent rules
3. NIST AI Risk Management Framework (U.S.)
Not mandatory but widely adopted. Sets guidelines for:
- Secure AI
- Transparent models
- Risk controls
4. Canada’s AIDA Act
Focuses on consumer transparency and safety.
5. U.S. Executive Order on AI (2023)
Requires:
- Safety testing
- Reporting
- Cybersecurity safeguards
If an enterprise uses AI, it must comply with at least one of these frameworks.
AI Governance Framework for Enterprises
An effective AI governance framework enterprise model includes:
1. Strategy
- Define business goals
- Identify AI use cases
- Set risk tolerance
2. Policies & Controls
Include rules for:
- Bias testing
- Privacy
- Security
- Human oversight
3. Data Governance
Ensure:
- Clean, high-quality data
- Metadata organization
- Classification and sensitivity tagging
4. Model Governance
Covers:
- Documentation
- Versioning
- Explainability
- Monitoring model drift
5. Operational Governance
Set guardrails for:
- Deployment
- Access control
- Incident response
6. Continuous Monitoring
Track:
- Output correctness
- Bias
- Performance
- Security vulnerabilities
This framework aligns with modern AI enterprise governance requirements.
AI Governance Implementation Challenges
Companies are eagerly experimenting with AI to revolutionize their operations and gain a competitive edge. Many are looking at the various applications of AI, but others are also expressing concerns about misinformation and disinformation.
To steer AI in the right direction, organizations must first understand the nuances and challenges of implementing AI governance.
Along with ethical guardrails and resources training, implementing AI governance comes with several data challenges:
- Complexity: AI systems are often complex and difficult to understand.
- Data quality issues: Ensuring high-quality, unbiased data is challenging.
- Regulatory compliance: Keeping up with evolving regulations requires a continuous effort.
Overcome AI Governance Challenges With a Data Governance Framework
Organizations must understand that the data they own and manage is fundamental to enabling them to pivot to AI initiatives. You can think of data as a magic key that unlocks the AI governance puzzle.
Ultimately, by focusing on key areas of data governance, organizations can expect reliable AI outcomes.
- Data quality: Data governance frameworks enhance data accuracy, completeness, enabling bias mitigation, ensuring reliable AI model training.
- Data privacy and security: Measures like access controls and encryption protect sensitive information and ensure privacy compliance.
- Improving transparency and accountability: Tracking data lineage and taking ownership increases transparency and accountability in AI systems.
- Policies and processes: Implementing clear policies and procedures for data governance ensures consistent and compliant AI operations.
How Can OvalEdge Help?
Data governance is a standalone step within AI governance. To become AI-ready, data must meet several unique requirements, which are achieved through data governance.
Related Post: AI Data Readiness vs Traditional Data Quality
OvalEdge is a company focused on AI data readiness. Our data governance solutions can help you start on the journey of AI governance by tackling the crucial first and last stages of a value chain activity.
We enable you to overcome input data issues at the source, as early as possible, before they infiltrate the data, models, and systems that constitute your AI ecosystem. Our tools enable you to catch and remedy input data issues early before they cause any potential flaws in the effectiveness of your AI output.
Our approach also focuses on output data governance.
FAQs
1. What is AI governance in simple words?
AI governance is the system of rules and controls that ensures AI is fair, safe, ethical, and compliant.
2. Why do companies need AI governance?
To prevent AI errors, reduce bias, maintain privacy, stay compliant, and protect the business from costly operational failures.
3. How is AI governance different from data governance?
Data governance manages data inputs and outputs, while AI governance manages the entire AI lifecycle data, models, systems, processes, and policies.
4. Which industries need AI governance the most?
Banking, healthcare, government, retail, insurance, and any industry using AI for decision-making.
5. What is included in an AI governance framework?
Policies, controls, model documentation, monitoring systems, data governance, risk assessments, and human oversight.
6. Does AI governance apply to GenAI tools like ChatGPT?
Yes, enterprises must define how GenAI tools are used, what data they access, and how outputs are monitored.
7. What happens if AI governance is ignored?
Risks include legal penalties, biased decisions, data breaches, system failures, and reputational damage.
8. How can organizations start with AI governance?
Begin with strong data governance, define AI policies, train teams, assess risk, and adopt tools like OvalEdge for monitoring.
Book a demo with us to find out:
|
Deep-dive whitepapers on modern data governance and agentic analytics

OvalEdge Recognized as a Leader in Data Governance Solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.