Table of Contents
Top Business Intelligence Tools in 2026: A Practical Buyer’s Guide
This blog explores the top business intelligence (BI) tools for 2026, highlighting their benefits, key features, and how to choose the right platform for your organization. It discusses how BI tools enhance decision-making, improve data governance, and boost efficiency. It also covers best practices for implementing BI solutions, with a focus on data intelligence platforms like OvalEdge for operational success.
You already know business intelligence tools can improve decision-making.
In fact, 91% of BI users say these tools significantly improve decisions, especially for financial reporting and planning, as per a ResearchGate report.
But if you’re being honest, your day-to-day experience probably doesn’t always match that promise.
You open a dashboard expecting clarity and walk away with more questions. Before acting, you double-check the data, ask for clarifications, or fall back on spreadsheets just to be safe. Over time, dashboards stop driving decisions and become reference points you don’t fully trust.
As data spreads across CRMs, ERPs, cloud platforms, and internal systems, this problem compounds. More data doesn’t automatically mean better insight.
Modern BI tools help by unifying data and surfacing trends in near real time. But real impact comes when that data is governed, well-defined, and trustworthy. That’s where data intelligence platforms like OvalEdge ensure BI delivers insights you can act on with confidence.
In this guide, you will learn how business intelligence tools benefit modern organizations, explore the top BI tools to consider in 2026, and understand how to choose and implement the right solution based on your data maturity, integration needs, and decision-making goals.
How do business intelligence tools benefit modern organizations?
Business intelligence tools help organizations turn raw data into actionable insights by unifying data from multiple sources, visualizing performance through dashboards, and enabling faster, more informed decision-making across teams. They improve visibility, efficiency, forecasting, and governance while supporting scalable, data-driven operations.
5 key benefits of BI tools
-
Faster and more confident decision-making: BI tools consolidate data from across the organization into a single view, allowing leaders and teams to track KPIs, compare performance, and make decisions based on consistent metrics rather than fragmented reports.
-
Improved operational efficiency through automated reporting: Automated dashboards and scheduled reports reduce manual data preparation and spreadsheet dependency. Teams spend less time assembling reports and more time acting on insights.
-
Enhanced data visibility across teams: By centralizing analytics dashboards, BI platforms ensure that sales, marketing, finance, and operations work from the same data definitions, reducing misalignment and conflicting interpretations.
-
Real-time monitoring of business performance: Modern BI software supports near real-time data refreshes, enabling teams to monitor operational metrics, identify anomalies early, and respond quickly to changes in demand or performance.
-
Stronger forecasting and trend analysis: BI tools make it easier to analyze historical patterns, identify trends, and support planning activities such as revenue forecasting, capacity planning, and budget allocation.
Top 5 business intelligence tools in 2026
Choosing the right business intelligence tool depends on how well it fits into your data ecosystem, supports decision-making workflows, and scales with growing data complexity. Below are six BI tools and platforms that organizations commonly evaluate in 2026, each serving a distinct role in modern analytics stacks.
1. Microsoft Power BI
Microsoft Power BI is a widely used business intelligence and analytics platform designed to help organizations visualize data, monitor performance, and share insights across teams. It is especially popular among companies already using the Microsoft ecosystem, as it integrates tightly with Azure, Excel, Microsoft 365, and Dynamics.
Power BI is positioned as a flexible BI tool that supports both self-service analytics for business users and enterprise-scale reporting for larger organizations. It is commonly used for operational dashboards, executive reporting, and departmental analytics.
Key features
-
Interactive dashboards and reports: Power BI enables users to build interactive dashboards with drill-downs, filters, and real-time visual updates, making it easier to track KPIs and explore performance trends.
-
Wide range of data connectors: The platform supports hundreds of native connectors for cloud services, databases, files, SaaS applications, and on-prem systems, allowing organizations to unify data from multiple sources.
-
Data modeling and transformation with Power Query: Power Query allows users to clean, transform, and shape data using a low-code interface, reducing dependence on external data preparation tools.
-
AI-assisted analytics and natural language querying: Power BI includes built-in AI capabilities such as automated insights, anomaly detection, and natural language questions that allow users to query data using plain English.
-
Real-time and scheduled data refresh: Organizations can configure real-time dashboards or schedule regular refresh cycles to keep reports up to date based on business needs.
Pros
-
Seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem
-
Strong balance between self-service analytics and enterprise reporting
-
Affordable pricing for small teams with scalable enterprise options
-
Large user community and frequent product updates
-
Good mobile support for dashboards and reports
Cons
-
Licensing and feature tiers can be complex to navigate
-
Advanced features often require Power BI Premium
2. Tableau
Tableau is a leading data visualization and business intelligence platform known for its ability to help users explore data visually and uncover insights through interactive dashboards. It is widely used by analytics teams and business users who prioritize visual analysis, storytelling, and exploratory analytics.
Tableau is commonly adopted by organizations that work with large datasets and cloud data warehouses and need flexible, highly interactive reporting for decision-making and presentations.
Key features
-
Advanced data visualization and dashboards: Tableau offers a drag-and-drop interface that allows users to build highly interactive dashboards with rich visual elements, filters, and drill-down capabilities.
-
Visual data exploration and storytelling: Users can explore data freely, identify patterns, and create data stories that guide stakeholders through insights using visual narratives.
-
Broad data source connectivity: Tableau connects to a wide range of data sources, including cloud warehouses, relational databases, files, and SaaS platforms.
-
Tableau Prep for data preparation: Tableau Prep helps users clean, combine, and prepare data before analysis, reducing reliance on external data transformation tools.
-
Embedded analytics and extensibility: APIs and extensions allow organizations to embed Tableau dashboards into applications and customize analytics workflows.
Pros
-
Industry-leading data visualization capabilities
-
Strong support for visual exploration and storytelling
-
Intuitive interface for business users
Cons
-
Licensing costs can be high at enterprise scale
-
Data modeling and governance require additional setup
3. Qlik Sense
Qlik Sense is a self-service business intelligence and analytics platform known for its associative analytics engine, which allows users to explore data freely without being constrained by predefined queries or hierarchies. This approach makes Qlik Sense well-suited for complex analytical use cases where users need to uncover hidden relationships in data.
It is commonly used by organizations that require flexible data discovery, hybrid cloud deployments, and advanced analytics beyond standard dashboarding.
Key features
-
Associative analytics engine: Qlik’s associative engine enables users to explore all possible relationships within data, highlighting both selected and unselected values to reveal insights that traditional query-based tools may miss.
-
Self-service dashboard creation: Users can build interactive dashboards and visualizations using drag-and-drop tools, supporting ad hoc analysis and guided analytics.
-
In-memory analytics and performance optimization: Qlik Sense leverages in-memory processing to deliver fast query performance, even when working with large and complex datasets.
-
Advanced data modeling and scripting: The Data Load Editor allows technical users to perform complex data transformations and modeling using scripting capabilities.
-
Flexible deployment options: Qlik Sense supports cloud, on-premises, and hybrid deployments, giving organizations control over their analytics infrastructure.
Pros
-
Powerful associative analytics for deep data exploration
-
Strong performance with in-memory analytics
-
Flexible deployment models
Cons
-
Steeper learning curve for non-technical users
-
Requires governance planning to avoid inconsistent metrics
4. Looker
Looker is a modern business intelligence and analytics platform built around a centralized semantic modeling layer called LookML. Rather than focusing only on dashboards, Looker emphasizes consistent metrics, governed data access, and scalable analytics on top of cloud data warehouses.
It is commonly used by organizations with strong data engineering capabilities that want to ensure metric consistency across teams and embed analytics into internal tools or products.
Key features
-
Semantic modeling with LookML: LookML allows teams to define business metrics, dimensions, and logic once and reuse them across dashboards and reports, ensuring consistent definitions throughout the organization.
-
Cloud-native analytics: Looker runs directly on top of cloud data warehouses such as BigQuery, Snowflake, and Redshift, avoiding data duplication and supporting large-scale analytics.
-
Governance and access controls: Centralized modeling and permission management help enforce data governance and prevent inconsistent or unauthorized data usage.
-
Embedded analytics and APIs: Looker supports embedding dashboards and analytics into applications, along with APIs for custom integrations and automation.
-
Version control and collaboration: LookML projects integrate with Git-based version control, enabling collaboration, change tracking, and structured development workflows.
Pros
-
Strong metric consistency through centralized modeling
-
Well-suited for cloud data warehouse environments
-
Built-in governance and access control capabilities
Cons
-
Requires LookML knowledge, which can slow adoption
-
Less intuitive for non-technical or casual users
5. Sisense
Sisense is a business intelligence and analytics platform designed primarily for embedding analytics into applications and products. It is commonly used by SaaS companies and product teams that want to deliver analytics directly to end users rather than relying only on internal dashboards.
Sisense combines traditional BI capabilities with a strong developer focus, allowing organizations to build highly customized and scalable analytics experiences.
Key features
-
Embedded analytics: Sisense enables dashboards and visualizations to be embedded directly into web and SaaS applications, allowing analytics to become part of the product experience.
-
Developer-friendly APIs and customization: Extensive APIs and customization options allow teams to tailor dashboards, visuals, and interactions to specific application needs.
-
Flexible data modeling and pipelines: Sisense supports complex data pipelines and transformations, making it suitable for environments with diverse and high-volume data sources.
-
Scalable analytics architecture: The platform is designed to handle large datasets and high concurrency, supporting growth as usage increases.
-
AI-assisted analytics: Sisense includes capabilities for natural language querying and automated insights to support deeper analysis.
Pros
-
Strong embedded analytics capabilities
-
Highly customizable for product and engineering teams
-
Scales well for large datasets and concurrent users
Cons
-
Implementation can be complex for non-technical teams
-
Higher setup effort for deeply customized use cases
How to choose the right BI tool for your organization
A structured evaluation approach helps avoid choosing a BI tool based only on features or popularity. These five steps focus on aligning analytics capabilities with business goals, data maturity, and long-term scalability.
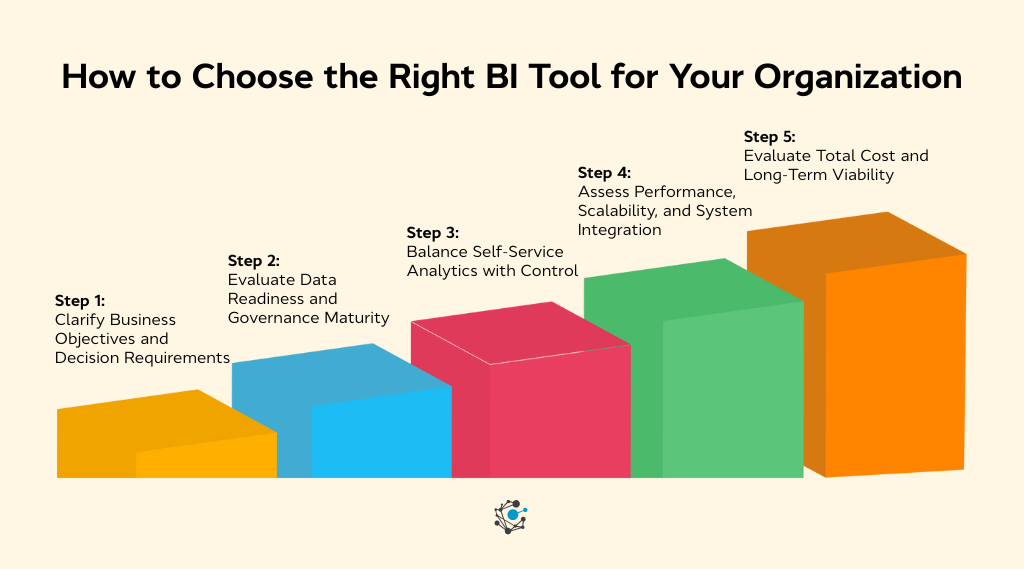
Step 1: Clarify business objectives and decision requirements
A BI tool should directly support the decisions your organization makes, not just generate reports. Without clear objectives, dashboards often become unused or misaligned with leadership priorities. Defining decision requirements ensures analytics stays relevant and actionable.
Actionable steps
-
Document the specific decisions each team needs to make using BI, such as budget allocation, pipeline forecasting, or operational planning.
-
Map these decisions to measurable KPIs and metrics that must be tracked consistently.
-
Rank use cases by business impact to guide tool prioritization and scope.
Step 2: Evaluate data readiness and governance Maturity
Even the most powerful BI tools struggle when data is fragmented, poorly defined, or inconsistent. Assessing data readiness helps determine whether your organization can support reliable reporting at scale. Governance maturity also affects adoption and trust in analytics outputs.
Actionable steps
-
Identify where data definitions differ across teams and systems, creating reporting conflicts.
-
Review how metadata, lineage, and ownership are currently managed across datasets.
-
Determine whether a data intelligence platform like OvalEdge is required to standardize and govern data before BI usage.
|
Pro Tip: If you’re unsure what “good governance” looks like in practice, OvalEdge’s Implementing Data Governance: Best Practices walks you through a proven framework to scope, operationalize, and scale governance without slowing analytics teams. It’s especially useful for organizations preparing data for BI adoption or modernization. |
Step 3: Balance self-service analytics with control
BI adoption increases when users can explore data independently without sacrificing accuracy or security. However, unrestricted self-service can lead to inconsistent metrics and duplicated logic. The right BI tool balances flexibility with centralized control.
Actionable steps
-
Test how easily business users can create or modify dashboards without IT support.
-
Evaluate how metric definitions and calculations are governed across reports.
-
Review role-based access controls to ensure sensitive data is protected.
Step 4: Assess performance, scalability, and system integration
As data volume and user adoption grow, BI performance becomes a critical success factor. Scalability ensures dashboards remain responsive and reliable across departments. Integration strength determines how smoothly the BI tool fits into your existing architecture.
Actionable steps
-
Validate query performance and dashboard load times using production-sized datasets.
-
Confirm compatibility with cloud warehouses, data pipelines, and identity systems.
-
Assess how the tool handles refresh frequency, concurrency, and peak usage.
Step 5: Evaluate total cost and long-term viability
The true cost of a BI tool extends beyond licensing fees. Long-term viability depends on how pricing, adoption, and operational effort scale over time. A forward-looking cost analysis helps avoid unexpected constraints.
Actionable steps
-
Calculate total cost based on creators, viewers, data volume, and refresh needs.
-
Factor in onboarding, training, and ongoing administration requirements.
-
Run a proof of concept to validate usability, performance, and ROI before final selection.
|
Pro Tip: For teams that need to justify governance investment alongside BI, OvalEdge’s whitepaper Building a Business Case for Data Governance outlines how organizations quantify value across efficiency, risk reduction, and analytics adoption. It’s particularly useful when presenting BI and governance initiatives to executive stakeholders. |
How to implement a BI tool successfully
A successful BI implementation is not defined by how fast dashboards go live, but by how consistently teams trust and use them. Organizations that treat BI as a data and governance initiative, not just a reporting project, see higher adoption and better decision outcomes.
1. Start with a clear analytics ownership model
BI initiatives fail when accountability is unclear. Defining ownership ensures decisions, not just reports, improve over time.
Actionable steps
-
Assign clear ownership for business metrics, dashboards, and data sources.
-
Define who approves metric definitions and changes before dashboards are published.
-
Align BI success metrics with business outcomes such as adoption and decision speed.
2. Prepare and govern data before it reaches BI
Most BI issues originate upstream in unmanaged data. Preparing and governing data before visualization reduces rework and rebuild cycles.
Actionable steps
-
Identify authoritative data sources for each reporting domain.
-
Standardize business definitions and calculation logic across systems.
-
Use a data intelligence platform like OvalEdge to catalog data, map lineage, and provide context before BI consumption.
3. Embed security, compliance, and access controls early
Security and compliance become expensive when added after BI adoption. Early controls protect data while enabling self-service analytics.
Actionable steps
-
Implement role-based access aligned with data sensitivity.
-
Document lineage and ownership for audit and impact analysis.
-
Automate governance workflows to avoid manual approvals and bottlenecks.
4. Launch with high-impact use cases first
Early wins build confidence and justify further investment. Starting small reduces risk and accelerates learning.
Actionable steps
-
Select one or two business-critical dashboards for the initial rollout.
-
Validate data accuracy and performance with real users.
-
Iterate quickly before expanding dashboards across teams.
5. Measure adoption and trust, not just usage
Dashboard views alone do not indicate success. Trust and repeat usage determine long-term BI value.
Actionable steps
-
Track dashboard usage alongside feedback and data issue reports.
-
Monitor how often metrics are questioned or revalidated.
-
Use data lineage and catalog insights from OvalEdge to proactively address trust gaps.
How OvalEdge strengthens BI implementations
BI tools work best when users understand where data comes from, how it changes, and what it means.
OvalEdge provides the data intelligence layer that ensures BI platforms operate on governed, trusted, and well-documented data. This reduces dashboard churn, improves adoption, and shortens the time from insight to action.
Here’s how OvalEdge strengthens BI outcomes:
1. Data Governance, Lineage, and Cataloging
OvalEdge provides comprehensive data governance by enforcing consistent data definitions and managing data lineage. This ensures that every dataset used by BI tools is traceable and accountable, eliminating confusion and errors that arise from inconsistent data sources.
2. Enhancing data quality
OvalEdge helps improve data quality by providing a unified view of all data assets. It standardizes and cleanses data before it enters BI tools, making sure that insights are based on trustworthy, high-quality data.
3. Cross-system visibility
For organizations with complex data ecosystems, OvalEdge offers cross-system visibility, enabling teams to track and understand how data flows between various platforms and systems. This transparency improves the accuracy and reliability of BI reports.
4. Ideal for complex data ecosystems and compliance needs
OvalEdge is particularly useful for organizations with intricate data environments or strict compliance requirements. Its robust metadata management, data governance capabilities, and ability to integrate across systems help ensure that BI implementations align with both internal and external regulatory standards.
If your BI rollout is slowing down due to inconsistent data, unclear definitions, or low confidence in reports, OvalEdge helps operationalize governance and trust across your BI ecosystem.
Book a demo to see how it fits into your BI implementation strategy.
Conclusion
Business intelligence tools are essential for turning data into decisions, but dashboards alone do not guarantee insight. When data lacks clarity, consistency, or trust, even the most advanced BI platforms struggle to deliver value.
The most effective BI programs focus on more than visualization. They prioritize data readiness, clear definitions, and governance across the analytics stack. By aligning BI tools with business goals, scalable architecture, and strong data foundations, organizations can improve adoption, reduce reporting friction, and make confident decisions at every level.
This is where data intelligence platforms like OvalEdge add measurable value. By cataloging data assets, mapping lineage, enforcing governance, and improving data quality before BI consumption, OvalEdge ensures your BI tools operate on reliable, well-understood data.
If your organization is evaluating BI tools or struggling with inconsistent dashboards, poor adoption, or low trust in reports, OvalEdge helps bridge the gap between raw data and meaningful analytics.
Book a demo to see how data intelligence can strengthen your BI strategy and accelerate decision-making.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a BI tool and a data intelligence platform?
BI tools focus on visualizing and reporting data, while data intelligence platforms manage data context, governance, lineage, and quality. Data intelligence ensures BI dashboards use trusted, well-understood data.
2. When should an organization invest in a BI tool?
Organizations should invest in BI when teams need consistent reporting, faster decision-making, and visibility across multiple data sources, especially when manual reporting or spreadsheets no longer scale.
3. Why do BI dashboards often show conflicting numbers?
Conflicts usually occur due to inconsistent data definitions, multiple data sources, or a lack of governance. Without standardized metrics and lineage, different teams interpret and calculate data differently.
4. Can multiple BI tools coexist in the same organization?
Yes. Many enterprises use multiple BI tools across teams. A data intelligence platform like OvalEdge helps standardize definitions, improve visibility, and maintain consistency across tools.
5. How long does it typically take to implement a BI tool?
Initial dashboards can be built in weeks, but full adoption often takes months. Timelines depend on data readiness, governance maturity, integration complexity, and user training.
6. How does OvalEdge support BI tools after implementation?
OvalEdge improves ongoing BI success by providing data cataloging, lineage, governance, and quality monitoring, helping teams trust reports, troubleshoot issues faster, and scale analytics with confidence.
Explore more best data governance practices and insights from industry leaders and experts

OvalEdge recognized as a leader in data governance solutions
.png?width=1081&height=173&name=Forrester%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
.png?width=1081&height=241&name=KC%20-%20Logo%201%20(1).png)
“Reference customers have repeatedly mentioned the great customer service they receive along with the support for their custom requirements, facilitating time to value. OvalEdge fits well with organizations prioritizing business user empowerment within their data governance strategy.”
Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Data and Analytics Governance Platforms, January 2025
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
GARTNER and MAGIC QUADRANT are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.


.png)
